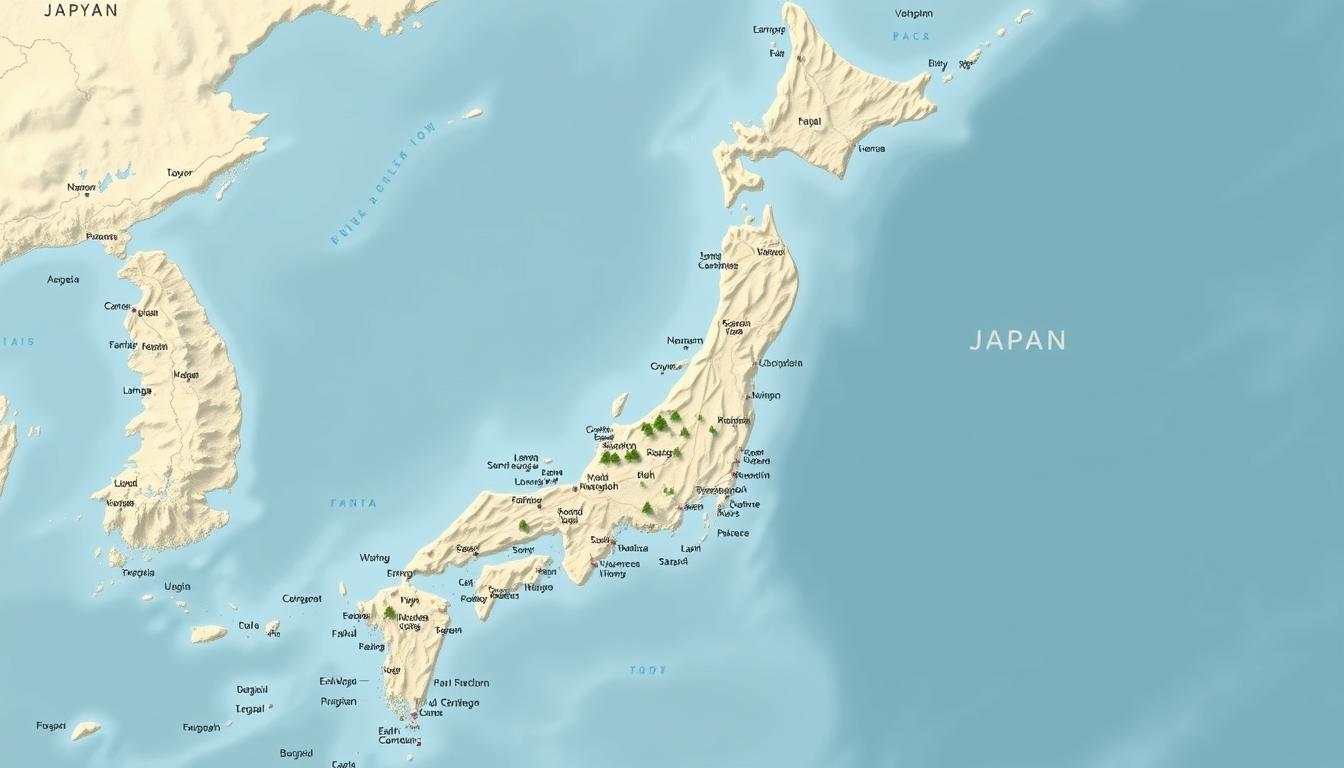
Japan is an archipelago located on the Pacific coast of East Asia. It stretches over 3,000 km and has 14,125 islands. The main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku.
Knowing Japan’s geography is key to exploring its varied landscapes. From busy cities to peaceful countryside, an interactive map is vital. It helps travelers, researchers, and anyone curious about Japan’s mix of old and new.
Japan is full of experiences waiting to be found. The interactive map is a detailed guide to its cities, islands, and geography. It’s perfect for planning a trip or doing research.
Understanding Japan’s Geographical Position
The Japanese archipelago, with over 6,800 islands, is in East Asia. This unique spot has shaped Japan’s history, culture, and economy.
Japan’s Location in East Asia
Japan sits in the northwestern Ring of Fire, on several tectonic plates. It’s between 20° to 45° north and 122° to 153° east. This makes Japan very prone to earthquakes.
Coordinates and Neighboring Countries
Japan is surrounded by seas. The Sea of Okhotsk is to the north, the Sea of Japan to the west, and the Pacific Ocean to the east. It’s close to China, Korea, and Russia, making it key in regional politics.
Strategic Importance in the Pacific
Japan’s spot in the Pacific Ocean is very important. It’s key for international trade and security. Its seas are vital for global shipping.
The Japanese Archipelago
The Japanese archipelago stretches over 3,000 km. It has diverse climates and ecosystems. This diversity shows in its rich cultural heritage and varied landscapes.
Japan’s Maritime Boundaries
Japan’s seas are defined by its exclusive economic zone (EEZ). This EEZ is huge in the Pacific Ocean. It’s vital for Japan’s fishing and offshore energy.
For a detailed map Japan, showing its cities, islands, and geography, many online resources exist. These maps give insights into Japan’s complex geography and its role in the country’s growth.
The Four Main Islands of Japan
Japan’s geography starts with its four main islands: Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, and Shikoku. These islands are the heart of Japan’s varied landscapes and culture.
Honshu: Japan’s Largest Island
Honshu is the biggest island and home to the most people. It has Tokyo, Osaka, and Kyoto, key cities. It’s the center of Japan’s economy and culture.
Major Regions and Cities
Honshu has different areas, each special in its own way. The Kansai region, with Osaka, Kobe, and Kyoto, is famous for its culture and history.
Geographical Features
The island has a wide range of landscapes. From the Japanese Alps to the Kanto region’s fertile plains. Mount Fuji, a symbol of Japan, is here.
Hokkaido: The Northern Frontier
Hokkaido is the northernmost island, known for its tough landscape and cold weather. It’s great for skiing and hiking.
Unique Climate and Landscape
Hokkaido’s weather is very cold in winter and mild in summer. Its beauty, with volcanoes and lakes, draws visitors from all over.
Kyushu: Gateway to Asia
Kyushu is in the southwest and was a key path to Asia. It’s famous for its volcanoes, hot springs, and Fukuoka, a big economic center.
Shikoku: The Smallest Main Island
Shikoku is the smallest island and known for its beautiful views and pilgrimage routes. The Shikoku Pilgrimage is famous here. It’s quieter than the other islands.
A famous geographer once said, “Japan’s islands are not just geographical entities but also carriers of the country’s rich cultural heritage.” The four main islands are key to understanding Japan’s geography and culture.
Japan’s Minor Islands and Island Groups
Japan is not just about its four main islands. It has many smaller island groups too. These islands add a lot to Japan’s culture and geography.
Okinawa and the Ryukyu Islands
The Ryukyu Islands, including Okinawa, have a special culture and history. Okinawa, the biggest island, is known for its stunning beaches and unique traditions.
Cultural and Geographical Distinctions
The Ryukyu Islands have their own culture, shaped by being an independent kingdom. Their location has also made their dialect and traditions different.
The Izu Islands
The Izu Islands are south of Tokyo and loved by tourists. They are famous for their natural beauty and hot springs. They offer a peaceful break from city life.
Other Notable Island Chains
Japan has many island chains, each special in its own way. The Ogasawara Islands, for example, are known for their biodiversity.
Ogasawara Islands
The Ogasawara Islands are a UNESCO World Heritage site. They are famous for their unique plants and animals. Their remote location has kept their beauty intact.
Disputed Territories
Some of Japan’s minor islands are in dispute. These disputes come from history and politics.
If you want to learn more about Japan’s minor islands, a Japan Map download is a great resource. It offers detailed geographical information.
Comprehensive Japan Map Guide
Exploring Japan’s geography needs a good map guide. The country has everything from busy cities to peaceful countryside. There are many maps to choose from, depending on what you need.
Political Maps of Japan
Political maps show Japan’s 47 prefectures. They help you understand the country’s government and plan trips.
Physical and Topographical Maps
These maps highlight Japan’s landscapes, like mountains and rivers. They’re great for outdoor fans and geography researchers.
Historical Maps of Japan
Historical maps reveal Japan’s past, including old boundaries and key events. They’re useful for historians and anyone curious about Japan’s history.
Where to Find Quality Japan Maps
You can find top-notch Japan maps online and offline.
Online Resources
Online, you can use digital map sites and websites with interactive maps. Google Maps and other map websites are popular choices.
Print Publications
For printed maps, check out atlases and travel guides. You can find them in bookstores or online at Amazon.
Whether you’re visiting Japan or just interested in its geography, a good map guide is key. By looking at different maps, you can learn more about this amazing country.
Major Cities on the Japan Map
Japan’s major cities, like Tokyo and Osaka, are famous for their lively culture and history. These cities are key to Japan’s economy. They also show the country’s rich past and modern progress.
Tokyo: The Capital Metropolis
Tokyo, the capital, is a world leader in tech, culture, and innovation. It’s famous for its cutting-edge technology and vibrant cultural scene.
Tokyo’s 23 Special Wards
The heart of Tokyo is split into 23 special wards. Each ward has its own vibe and attractions. From Shibuya’s busy streets to Asakusa’s old temples, Tokyo’s wards offer a wide range of experiences.
Greater Tokyo Area
The Greater Tokyo Area goes beyond the 23 wards. It includes Yokohama and Kawasaki. This area is a big economic and cultural center, with over 38 million people.
Osaka and the Kansai Region
Osaka is famous for its food, fun, and nightlife. The Kansai region, which includes Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe, is full of culture and history.
Kyoto: The Cultural Heart
Kyoto is a city that keeps Japan’s culture alive. It’s full of temples and gardens. It’s a top spot for those who love history and traditional Japanese culture.
Other Major Urban Centers
Japan has more major cities, each with its own special charm.
Yokohama and Kawasaki
Yokohama is Japan’s second-largest city, known for its port and international vibe. Kawasaki, between Tokyo and Yokohama, is an industrial city with a rich culture.
Nagoya and Central Japan
Nagoya is a big industrial center and home to Toyota. Central Japan, including Nagoya, is known for its manufacturing and tech.
Sapporo and Northern Cities
Sapporo, on Hokkaido, is famous for its snowy winters and the Sapporo Snow Festival. Other northern cities offer unique experiences, from nature to culture.
These cities are key on the Japan map. They play big roles in Japan’s economy, culture, and daily life. For those exploring Japan, a printable Japan Map is very helpful. It helps navigate these cities and their attractions.
Japan’s Mountainous Terrain
The mountains of Japan are truly unique, with peaks and volcanoes that hold cultural and environmental value. Over 75% of Japan is covered in mountains, making them a key part of the country’s geography.
The Japanese Alps
The Japanese Alps stretch through central Honshu, Japan’s largest island. They are famous for their stunning views and varied ecosystems. The Alps are split into three main ranges:
- Northern Alps (Hida Mountains)
- Central Alps (Kiso Mountains)
- Southern Alps (Akaishi Mountains)
Northern, Central, and Southern Alps
Each part of the Japanese Alps has its own charm. The Hida Mountains are known for their rugged peaks. The Kiso Mountains boast beautiful valleys. The Akaishi Mountains, in the Southern Alps, are a favorite among hikers for their natural beauty.
Mount Fuji and Iconic Mountains
Mount Fuji, Japan’s highest peak, is a symbol of the country. It’s considered sacred and has inspired many artists and poets. Other notable mountains include Mount Zao, famous for its ski resorts, and Mount Aso, an active volcano in Kyushu.
Volcanic Regions and Activity
Japan sits on the Pacific Ring of Fire, making it very active volcanically. Its volcanic areas are filled with active volcanoes and geothermal features.
Active Volcanoes
Mount Aso in Kyushu and Mount Sakurajima are two of Japan’s most active volcanoes. They are watched closely because of their impact on nearby communities.
Geothermal Features
Japan’s volcanic areas also have hot springs (onsen) and volcanic gas emissions. These features are of scientific interest and boost Japan’s tourism and cultural heritage.
Rivers, Lakes, and Coastlines of Japan
Japan’s geography is complex, with many rivers, lakes, and coastlines. These are key for its biodiversity and economy. They support agriculture, industry, and cities.
Major River Systems
Japan has important river systems. They are vital for its ecosystem and economy. The rivers help with farming, industry, and cities.
Shinano, Tone, and Ishikari Rivers
The Shinano River is Japan’s longest, over 367 kilometers. It’s a major water source for farming and industry. The Tone River is known for its complex system and role in controlling floods. The Ishikari River is the third-longest and key for the local ecosystem.
| River Name | Length (km) | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Shinano River | 367 | Longest river, vital for irrigation and industry |
| Tone River | 322 | Complex river system, significant for flood control |
| Ishikari River | 268 | Important for regional ecosystem |
Notable Lakes and Inland Waters
Japan has many lakes, with Lake Biwa being the largest. These lakes are vital for biodiversity and water supply.
Lake Biwa and Other Significant Lakes
Lake Biwa is Japan’s largest freshwater lake and one of the oldest. It supports a wide range of aquatic life. Other notable lakes include Lake Kasumigaura and Lake Saroma.
Japan’s Diverse Coastlines
Japan’s coastlines along the Sea of Japan and Pacific Ocean are diverse. They are important for fishing and tourism.
Sea of Japan Coast
The Sea of Japan coast is rugged and scenic. It attracts tourists and supports local fishing.
Pacific Ocean Coast
The Pacific Ocean coast is complex, with many bays and inlets. It supports a rich marine biodiversity.
Japan’s Climate Regions
Japan has different climate zones due to its unique geography. The climate changes a lot from north to south. It goes from temperate to subtropical.
Northern Climate Zones
Hokkaido, Japan’s northern island, is very cold and snowy in winter. It’s great for winter sports because of all the snow. But, summers there are mild and nice.
Central Japan’s Climate
Central Japan, like Tokyo, has a temperate climate. It has four clear seasons. Summers are hot and humid, while winters are mild. This area is very crowded with big cities like Tokyo and Nagoya.
Southern and Subtropical Regions
The southern parts, including Okinawa, have a subtropical climate. Okinawa is famous for its warm weather and high humidity all year.
Okinawa’s Unique Climate
Okinawa’s subtropical climate draws many tourists, even in winter. It’s warmer than the rest of Japan. Its location near the equator and the ocean affects its climate.
Seasonal Weather Patterns
Japan’s climate has clear seasons. Spring brings cherry blossoms, summer is hot, autumn has beautiful leaves, and winter has snow in the north. Knowing these patterns helps plan trips and activities in Japan.
Administrative Divisions on the Japan Map
Knowing Japan’s administrative divisions is key to understanding its geography. It helps in finding important places on a Japan map. Japan is split into 47 prefectures, which are the main administrative areas.
Japan’s 47 Prefectures
The 47 prefectures of Japan are divided into types. These include To (metropolitan prefecture), Do, Fu (urban prefecture), and Ken (rural prefecture). This division is essential for grasping Japan’s administrative setup.
Prefecture Types: To, Do, Fu, and Ken
Tokyo is a “To,” or metropolitan prefecture. Osaka and Kyoto are “Fu,” or urban prefectures. Most prefectures are “Ken.” Knowing these types helps in using a Japan Map outline.
Major Regions and Their Characteristics
Japan’s prefectures are grouped into major regions. Each region has its own special features. The Kanto region, home to Tokyo, is a major economic center.
Kanto, Kansai, Tohoku, and Others
The Kansai region, with Osaka, Kyoto, and Kobe, is rich in culture. Tohoku is known for its natural wonders. Hokkaido is famous for its landscapes and farming. These regions are important for Japan’s geography and economy.
Special Administrative Areas
Japan also has special administrative areas. These areas have unique setups. They add to the complexity of Japan’s administrative scene.
Natural Hazards and Geographical Challenges
Japan’s location on the Pacific Ring of Fire puts it at risk for many natural hazards. Its geography, with islands and tectonic activity, makes it prone to disasters.
Earthquake Zones and Tectonic Activity
Japan sits at the meeting of four tectonic plates, making it very seismically active. Knowing the earthquake zones is key for being ready for disasters.
The Pacific Ring of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a zone of intense seismic and volcanic activity. It goes from New Zealand, through Asia, the Philippines, Japan, and the Aleutian Islands, to the western coasts of North and South America. Japan’s spot in this zone makes it very likely to have earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Major Historical Earthquakes
Japan has seen many big earthquakes, like the 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami. Looking at these events helps improve how we respond to disasters.
Tsunami-Prone Areas
The Japanese coast is at risk for tsunamis, often caused by earthquakes. Knowing which areas are most at risk is important for coastal communities and for making good early warning systems.
Other Natural Disaster Risks
Japan also faces risks from typhoons, flooding, and landslides, aside from earthquakes and tsunamis.
Typhoons and Flooding
Typhoons hit Japan often, bringing heavy rain that can cause flooding and landslides. Having plans, like those on a Japan Map printable, can help reduce these dangers.
Landslides and Erosion
Heavy rain and deforestation can cause landslides and erosion. These are big risks for communities and buildings.
Printable and Educational Japan Maps
Exploring Japan? You’ll need top-notch, printable maps. They’re great for learning and planning trips.
High-Resolution Printable Maps
High-resolution maps of Japan are perfect for studying. They show the country’s geography in detail.
Outline Maps for Educational Use
Outline maps are great for school. They help students learn about Japan’s geography by labeling areas.
Detailed Regional Maps
Detailed regional maps give a close-up look at Japan. They highlight local landmarks and transport.
Specialized Maps for Different Purposes
Specialized maps meet various needs. For example, tourism maps show popular spots.
Tourism and Travel Maps
Tourism maps guide visitors around Japan. They point out key places and amenities.
Language and Cultural Maps
Language and cultural maps explore Japan’s heritage. They show linguistic and cultural differences.
Japan Map Downloads and Formats
Japan maps come in many digital formats. You can download them for learning, planning, or fun.
Transportation Networks Across Japan
Japan’s transport system is a wonder of modern engineering. It links major cities and remote islands with rail, road, and air travel. This network helps locals and tourists travel efficiently across the country.
The Shinkansen and Rail Systems
The Shinkansen, Japan’s famous bullet train, shows the country’s tech progress and love for being on time. It zooms at up to 320 kilometers per hour, making travel fast and comfy.
Major Rail Lines and Connections
The Shinkansen is backed by a wide rail network that reaches small towns and cities. Companies like JR East, JR Central, and JR West run these lines, covering the whole country.
Highway and Road Networks
Japan also boasts a well-built highway and road system. From fast expressways to local roads, it’s easy to travel by car or bus to any corner of the country.
Maritime and Air Transportation Hubs
Japan’s location makes it key in international maritime trade. Its big ports and harbors are vital for shipping goods and people.
Major Ports and Harbors
Yokohama, Nagoya, and Kobe are among the world’s busiest ports. They handle a huge amount of cargo and passengers. These ports have top-notch facilities for efficient goods handling.
International and Domestic Airports
Japan has major airports like Tokyo’s Narita and Haneda, Kansai International, and Chubu Centrair. These airports are key for both domestic and international flights, connecting Japan to the globe.
Knowing Japan’s transport networks is key for getting around, whether you’re a tourist or a business traveler. Japan’s systems make it simple to see its cities, countryside, and more.
Conclusion: The Evolving Geography of Japan
Japan’s geography is always changing due to nature and human actions. It’s key to understand these shifts for planning and growth. A detailed map of Japan is essential. It gives us a clear view of the country’s varied landscapes, climate, and natural wonders.
Japan spans 377,973.89 km² and is home to 14,125 islands. Its terrain is rough, volcanic, and mountainous. The country boasts 108 active volcanoes, a diverse climate, and a 29,751 km coastline. As Japan grows and faces environmental changes, detailed maps and GIS will be more important than ever.
The mountains, rivers, and lakes in Japan greatly influence its climate, economy, and culture. A detailed map of Japan can pinpoint areas at risk from natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis. It helps in planning for a sustainable future.