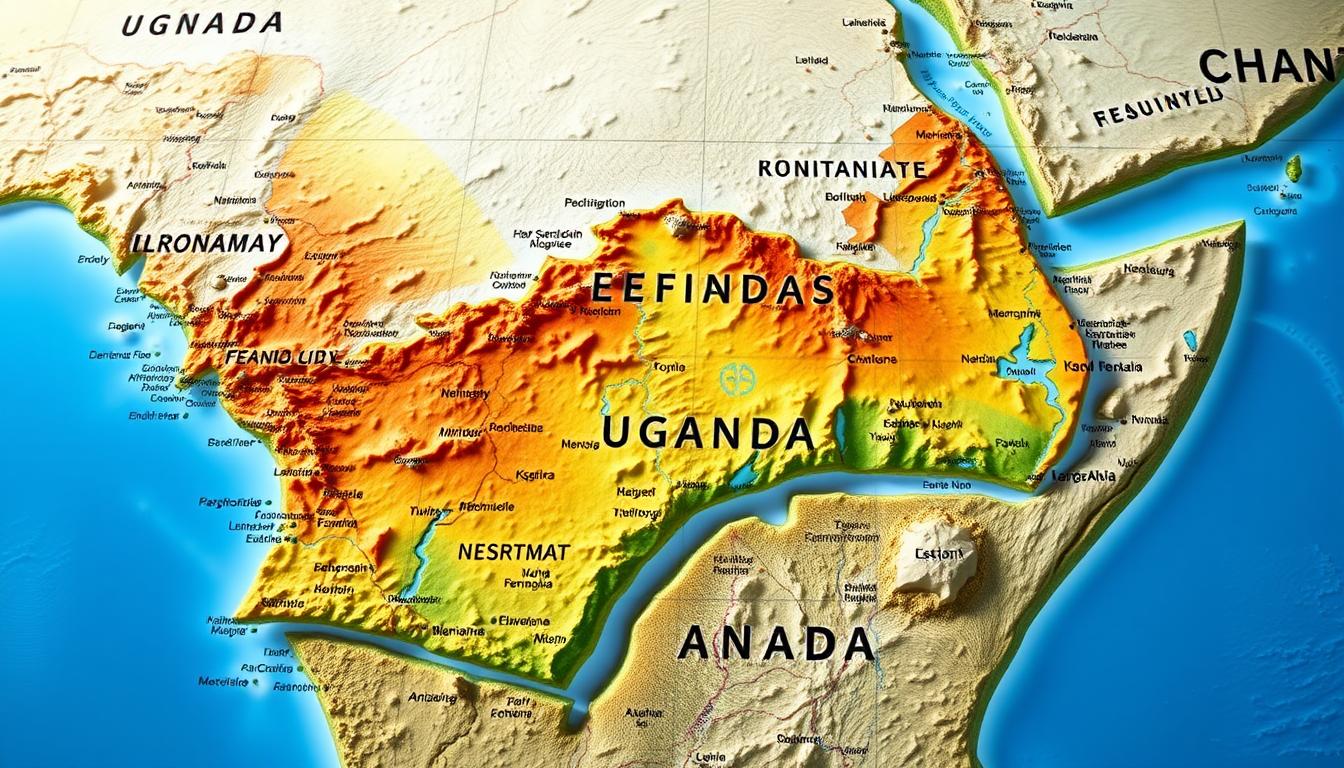
The East Africa region is full of different landscapes and countries. It includes Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. Knowing the area’s layout helps us understand its history, culture, and economy.
Uganda is right in the middle of this region. It has borders with several countries, making its location very important. Its borders with Kenya and others greatly affect the region’s relationships.
A detailed map of the region is key to understanding Uganda’s borders. This article will give you a full view of Uganda’s borders and their role in East Africa’s geography.
The Geographical Scope of East Africa
East Africa is a complex region with many countries and territories. It covers a wide area with different landscapes and cultures.
Countries That Comprise East Africa
The East African region has 18 countries and 4 territories, as the UN geoscheme shows. The core members form the East African Community. This group is important for the region’s economy and politics.
Core East African Community Members
The core members are Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda. They work together to improve regional ties and cooperation.
Extended East African Region
The extended region includes countries like Burundi, Rwanda, and South Sudan. This area is known for its varied geography and complex politics.
| Country | Capital | Population (millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Kenya | Nairobi | 53 |
| Tanzania | Dodoma | 61 |
| Uganda | Kampala | 45 |
Knowing about East Africa’s geography helps us understand its complexities. It shows the region’s varied landscapes and cultures.
Comprehensive East Africa Map: Regional Overview
A detailed East Africa map is key to understanding the region. It shows political boundaries, physical features, and where people live.
Political Boundaries and National Territories
The East Africa political map shows country lines, like those of Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, and Burundi. These lines help us see the region’s politics.
Major Physical Features Defining the Region
East Africa has many physical features. These include the Great Rift Valley, mountain ranges like the Rwenzori, and big lakes like Victoria and Tanganyika.
Population Distribution and Major Urban Centers
People in East Africa live in different places. There are more people in cities and fewer in the countryside.
Capital Cities and Their Locations
Big cities like Kampala (Uganda), Nairobi (Kenya), and Dar es Salaam (Tanzania) are important. They are centers of economy and politics.
Regional Population Density Patterns
| Country | Capital City | Population Density (per km²) |
|---|---|---|
| Uganda | Kampala | 173 |
| Kenya | Nairobi | 82 |
| Tanzania | Dodoma | 67 |
The table shows how many people live in different East African countries. It shows how people are spread out.
Uganda’s Position in the Heart of East Africa
Uganda is at the heart of East Africa, playing a key role in regional affairs. It’s bordered by Kenya to the east, Tanzania to the south, and Rwanda to the southwest. The Democratic Republic of the Congo lies to the west, and South Sudan to the north.
Geographical Coordinates and Total Land Area
Uganda’s location is between 1°S and 4°N latitude, and 29°E and 35°E longitude. It spans about 241,551 square kilometers. This makes it a big player in the East Africa region.
Landlocked Status and Its Economic Implications
Uganda is landlocked, relying on neighbors for port access and trade. This affects its economy, as trade costs and efficiency depend on its connections with Kenya and Tanzania.
Uganda’s Administrative Regions and Districts
Uganda is split into four main regions: Central, Eastern, Northern, and Western. These are divided into over 100 districts.
Central, Eastern, Northern, and Western Regions
Each region has its own traits and economic focus. For example, the Central Region hosts Kampala, the capital. The Eastern Region is known for its farming.
Major Cities and Their Proximity to Borders
Kampala and Entebbe are in the Central Region, near borders. Other key towns are also close to borders, boosting trade and cultural exchange.
Uganda’s strategic location in East Africa highlights its role in regional affairs and economy. Knowing its geography and divisions is key to understanding the region’s complexities.
Uganda-Kenya Border: The Eastern Frontier
The eastern frontier of Uganda, shared with Kenya, is key for both geography and economy. This area has varied landscapes and is vital for trade and travel.
Border Length and Geographical Characteristics
The Uganda-Kenya border spans different terrains, like mountains and lakesides. It includes Mount Elgon and the northern Lake Victoria shore.
Mount Elgon Region
The Mount Elgon area is famous for its biodiversity and beauty. It’s a big deal for both countries, boosting tourism and conservation.
Lake Victoria Northern Shore
The northern Lake Victoria shore is also important. It’s a big spot for fishing and helps the local economy.
Major Border Crossing Points and Infrastructure
There are key border crossings for trade and travel. Busia and Malaba are among the busiest.
| Border Crossing | Location | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Busia | South of Busia town | Major trade route |
| Malaba | North of Malaba town | Key commercial crossing |
Economic Corridors and Trade Routes
The Uganda-Kenya border has important economic paths. The Busia-Malaba corridor is a major trade route.
Busia-Malaba Transportation Corridor
This corridor links big towns and cities. It’s key for moving goods and people, boosting the economy.
Cross-Border Market Activities
Markets on both sides of the border are lively. They trade in things like food and crafts.
Kenya’s Western Border with Uganda: A Closer Look
Kenya’s western border with Uganda is complex. It involves geography, culture, and economy. The area has diverse natural resources and ethnic communities. These factors are important for both countries’ economies.
Kenya’s Western Counties Bordering Uganda
Kenya’s western counties bordering Uganda are Busia, Bungoma, and Trans Nzoia. They are known for fertile land and cross-border trade. The counties also have ethnic communities tied to Uganda.
Shared Natural Resources and Conservation Areas
The border region is rich in natural resources. It includes water bodies and wildlife. Lake Victoria, though not directly on the border, affects the climate and ecosystem.
Conservation areas like national parks are present. They promote tourism and biodiversity. “The conservation of natural resources is key for the ecosystem and local livelihoods,” a conservation expert notes. Kenya and Uganda work together to protect these areas.
Cultural Connections Across the Border
The border region has shared ethnic communities and cultural practices. This shared heritage helps in cross-border interactions and cooperation.
Shared Ethnic Communities
Communities like the Luhya and Teso have members on both sides. This fosters unity and cooperation. They share cultural practices, languages, and traditions.
Cross-Border Cultural Exchanges
Cultural exchanges are common. Events like traditional festivals and ceremonies involve both countries. These exchanges promote cultural understanding and boost tourism.
The region’s cultural heritage and natural beauty are vital. They offer opportunities for cooperation in tourism, conservation, and economic development for Kenya and Uganda.
Uganda-Tanzania Border: The Southern Connection
The Uganda-Tanzania border is key in East Africa. It’s important for trade and travel. It connects the two countries, sharing goods, services, and cultures.
Border Length and Key Geographical Features
The border is about 396 kilometers long. Lake Victoria is a major natural boundary. It’s a source of livelihood for border communities, with fishing and maritime connections.
Lake Victoria’s Role as a Natural Border
Lake Victoria is a key part of the border. It makes border management easier. It also boosts local economies through fishing and tourism.
Major Crossing Points and Border Towns
There are many crossing points and towns for trade and travel. These include:
Mutukula Border Post
Mutukula is a busy border post. It’s known for quick customs and lots of trade. It’s a key link for goods transport.
Lake Victoria Maritime Connections
Lake Victoria connects Uganda and Tanzania by sea. Ferries and boats carry goods and people. It’s vital for lake shore communities, giving access to markets and services.
| Border Post | Type of Traffic | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Mutukula | Road | Major trade route |
| Lake Victoria | Maritime | Fishing and tourism |
Uganda-Rwanda Border: The Southwestern Frontier
The Uganda-Rwanda border in the southwestern part of Uganda is key. It’s a vital part of the East Africa region. It affects the area’s economy and politics.
Geographical Characteristics and Border Length
The border between Uganda and Rwanda is about 169 kilometers long. It has hills and valleys. These features shape the local weather and farming.
Katuna/Gatuna and Other Major Crossing Points
Katuna/Gatuna is a major spot for trade between Uganda and Rwanda. Other important places include Mirama Hills and Cyanika. They help with both business and personal connections.
Economic and Political Significance
The Uganda-Rwanda border is very important. It’s key for regional unity efforts.
East African Community Integration
Uganda and Rwanda are working together through the East African Community. The border helps move goods and services. This boosts trade in the area.
Recent Border Tensions and Resolutions
There have been times of trouble at the border. But, diplomats have helped solve these issues. This keeps the border open for people and goods.
Uganda-Democratic Republic of Congo Border: The Western Challenge
The border between Uganda and the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is complex. It faces both geographical and security challenges. These issues arise from its varied landscapes and valuable natural resources.
Geographical Complexity and Length
The Uganda-DRC border spans different landscapes. It includes the Lake Albert region and the Rwenzori Mountains section.
Lake Albert Region
The Lake Albert region is key to the border. It offers fishing and hydrocarbon reserves. The lake’s shores are shared, making cooperation on resource use essential.
Rwenzori Mountains Section
The Rwenzori Mountains section is vital. It’s known for its biodiversity and tough terrain. Managing this area well is important for its ecological health.
Security Challenges and Management
The border area has security issues. Armed groups and cross-border crime are present. Uganda and the DRC must work together to manage these problems.
Natural Resources and Cross-Border Trade
The border region has many natural resources. These resources affect trade between the two countries.
Formal and Informal Border Economies
Both formal and informal economies exist along the border. They trade goods like agricultural products, minerals, and fuel. The informal economy, though big, often lacks regulation.
Resource-Related Border Disputes
Disputes over resources like oil and minerals cause tension. Diplomatic efforts and cooperation are needed to solve these issues.
The Uganda-DRC border is a key area for regional stability and economy. Overcoming challenges and using opportunities here needs ongoing cooperation and effective management.
Uganda-South Sudan Border: The Northern Boundary
The Uganda-South Sudan border is key to the region’s geography and politics. It has a rich history and plays a big role today. It affects the area’s politics and helps with humanitarian work.
Historical Formation and Current Status
The border was set during colonial times and has changed with the area’s politics. Now, it’s a major line between Uganda and South Sudan. It impacts trade, security, and cultural exchanges.
Major Crossing Points and Infrastructure
There are key crossing points along the border. These help move goods and people. They are:
- Oraba
- Malaba
- Vurra
These spots are vital for trade in the region. They need good infrastructure to handle traffic well.
Humanitarian Considerations and Refugee Movements
The border is also important for helping refugees. Uganda has taken in many from South Sudan, giving them shelter and aid.
Refugee Settlements Near the Border
Places like Rhino Camp and Imvepi refugee settlements are near the border. They house thousands of refugees from South Sudan’s conflict.
International Aid Corridors
International aid corridors are essential for helping refugees. They help move aid to those who need it most. This ensures critical help reaches the right people.
| Crossing Point | Location | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Oraba | Northern Uganda | Major trade route |
| Vurra | West Nile region | Key refugee crossing point |
As South Sudan’s situation changes, the border remains critical. It’s key for the region’s stability and humanitarian efforts.
Physical Features on the East Africa Map
The physical landscape of East Africa is a mix of different features. These include the Great Lakes system and mountain ranges. They are key for the region’s ecology and economy.
The Great Lakes System
The Great Lakes system is a standout in East Africa’s geography. It has several major lakes. These lakes are vital for the ecosystem and support the economy.
Lake Victoria Basin
Lake Victoria is the largest lake in Africa. It’s a big part of the Great Lakes system. It supports a huge fishing industry and is a key source of freshwater.
Lakes Albert, Edward, and Kyoga
Lakes Albert, Edward, and Kyoga are also part of the Great Lakes system. They are known for their rich biodiversity. They also boost the regional economy through tourism and fishing.
Mountain Ranges and Highlands
East Africa has several important mountain ranges and highlands. These areas are not just ecologically significant. They also draw tourists from all over.
Rwenzori Mountains and Mount Elgon
The Rwenzori Mountains, also called the “Mountains of the Moon,” and Mount Elgon are notable. They are known for their unique biodiversity. They also offer great hiking and climbing opportunities.
Virunga Mountains and Volcanic Features
The Virunga Mountains include volcanic peaks like Mount Nyiragongo. They are known for their volcanic activity and unique geological features.
The Great Rift Valley System in East Africa
The Great Rift Valley system runs through East Africa. It shapes the region’s landscape and affects its climate. It’s known for its geological significance and is home to many national parks and wildlife reserves.
Rivers and Watersheds Defining East African Borders
The network of rivers and watersheds is key in setting East Africa’s borders. This area’s geography is shaped by major water features. These features affect the politics and economies of the countries here.
The Nile River System and Its Tributaries
The Nile River system is a major feature in East Africa. It has many tributaries that add to its vast watershed. The White Nile, a main tributary, flows through Uganda.
White Nile’s Journey Through Uganda
The White Nile is vital for Uganda’s ecosystem and economy. It starts from Lake Victoria. Lake Victoria is also a key geographical feature.
Lake Victoria as a Source
Lake Victoria is Africa’s largest lake and a main Nile source. It’s shared by several East African countries. This makes it a key part of the region’s hydrology and a source of fresh water.
Other Significant River Systems
Other river systems also shape East Africa’s geography. Rivers flowing into Lake Victoria and other lakes support biodiversity and local economies.
Watershed Management and Transboundary Water Issues
Managing watersheds and shared water resources is a big challenge in East Africa. Countries must work together to use these resources sustainably. This helps avoid conflicts.
Historical Evolution of Uganda’s Borders
Historical events have shaped Uganda’s borders. The country’s borders were influenced by pre-colonial divisions, colonial rule, and post-independence changes.
Pre-Colonial Territorial Boundaries
Before colonial rule, Uganda was home to many ethnic groups and kingdoms. Each had its own territory. These divisions helped form the modern borders.
Colonial Border Demarcation Under British Rule
The British changed Uganda’s borders during their rule. They drew lines that ignored traditional territories. This created the modern state of Uganda.
Post-Independence Border Adjustments and Disputes
After gaining independence, Uganda faced border disputes with neighbors. These were solved through talks and sometimes international help.
Resolution Mechanisms for Border Conflicts
Border conflicts were tackled through agreements and regional cooperation. These efforts aimed to stabilize the area and boost economic ties.
Current Border Status and Management
Today, Uganda works with its neighbors to manage its borders. The East African Community helps with border management and regional integration.
The history of Uganda’s borders shows the complex mix of history, politics, and society. Knowing this history helps us understand the East Africa region today.
East Africa Travel Map: Planning Cross-Border Journeys
The East Africa travel map is key for exploring the region. It shows transportation routes and border crossings. East Africa’s roads, railways, and borders need careful planning to travel well.
Major Transportation Routes Connecting Uganda to Neighbors
Uganda is in the heart of East Africa, making it a key transportation hub. Its roads connect it to Kenya, Tanzania, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Road Networks and Conditions
East Africa’s roads have improved a lot. The Kampala to Nairobi highway is a major trade route between Uganda and Kenya. But, road conditions change, so always check before traveling.
Railway Connections and Development
The East African Railway Network is being built to improve regional connections. It’s expected to make trade and economic integration better.
“The revival of the railway network is expected to boost trade and economic integration in the region.” –
Border Crossing Procedures and Requirements
Knowing border crossing procedures is important for smooth travel. Make sure you have the right documents, like passports and visas. Each border post has its own rules, so research them well.
Travel Advisories and Safety Considerations
Travel safety in East Africa is a big concern. Keep up with local conditions and travel advisories from your country. Health and vaccination needs, and border region security, are also important.
Health and Vaccination Requirements
Check health advisories and make sure your vaccinations are current before traveling. Some vaccinations, like for yellow fever, might be needed.
Security Situation at Border Regions
Border regions can be risky due to conflict and unrest. Stay informed and be careful when traveling through these areas.
Economic Integration Across East African Borders
The East African Community common market has boosted economic ties across the region. It allows for the free flow of goods, services, and people. This has strengthened economic cooperation among member states.
East African Community Common Market
The East African Community common market has been key in promoting economic unity. It has removed tariffs and trade barriers. This has made a single market for all member states.
Cross-Border Trade Statistics and Trends
Cross-border trade has grown a lot, with trade volumes increasing among East African countries. This growth is due to easier trade procedures and lower tariffs.
| Year | Trade Volume (USD) | Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 10 billion | 5% |
| 2021 | 12 billion | 10% |
| 2022 | 14 billion | 15% |
Infrastructure Development Projects
Infrastructure development is vital for economic integration. Key projects include:
East African Standard Gauge Railway
The East African Standard Gauge Railway is a major project. It aims to improve transportation links among member states. This will help trade and economic integration.
Border Post Modernization Initiatives
Modernizing border posts has made cross-border trade smoother. It has reduced clearance times and costs.
Digital and Physical Maps of East Africa
East Africa’s varied landscapes are shown in digital and physical maps. These maps meet different needs and purposes. They cover mountains, valleys, and more.
Online Mapping Resources for East Africa
Digital maps are now more popular because they’re easy to access and update quickly. Online platforms offer interactive maps. These are great for navigation, research, and learning.
Specialized Maps for Different Purposes
There are maps for every need. Political and administrative maps show borders and divisions. Topographical maps focus on the land’s features.
Political and Administrative Maps
These maps are key for understanding East Africa’s politics. They show borders, capitals, and big cities.
Topographical and Physical Feature Maps
Topographical maps highlight the area’s varied landscapes. They include mountains, valleys, and water bodies. These maps help with environmental studies and planning.
Recent Cartographic Developments and Technologies
New cartography and GIS tech have made maps more accurate and accessible. Satellite imagery and GPS data are key. They give detailed views of East Africa’s geography.
Conclusion: Understanding Uganda’s Place in East Africa
Uganda is a key player in East Africa. Its diverse geography, economy, and culture add to the region’s complexity. The country’s location, bordered by several nations, makes it a vital trade and cultural hub.
Looking at the East Africa Map, Uganda’s central position is clear. It connects different countries and economies. The Great Lakes System and the Nile River add to its economic and cultural importance.
To truly understand Uganda’s role, we must grasp the regional dynamics. The East African Community promotes economic integration. Uganda’s contributions will be essential as the region evolves.