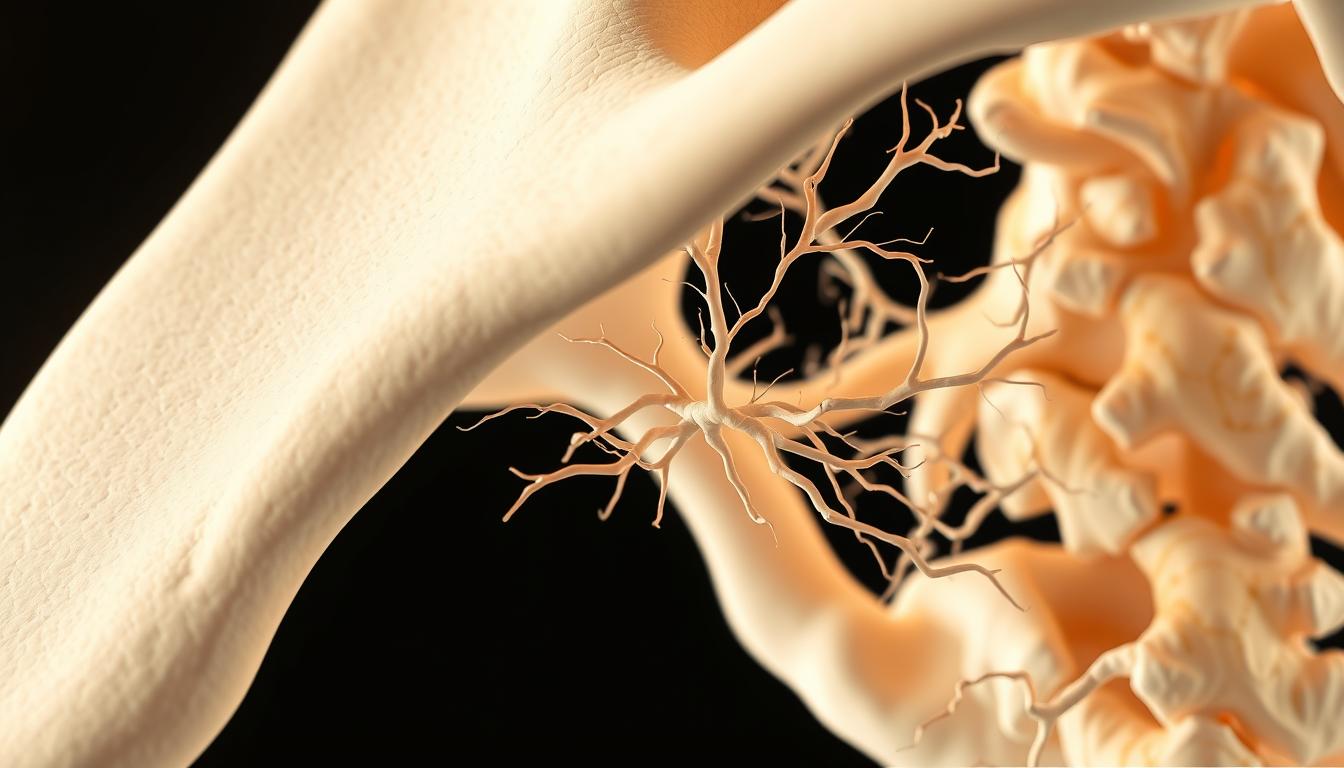
The human skeletal system is complex, giving support and protection to organs. A key part of bone anatomy is Volkmann’s Canals. These are special arrangements in cortical bones.
These canals let blood vessels reach the bones from the periosteum. They play a big role in bone structure and function. Knowing about Volkmann’s Canals helps us understand the bone structure better.
Volkmann’s Canals are important for bone health. They help supply nutrients and oxygen to the bone tissue.
What Is Volkmann’s Canal?
Volkmann’s Canal is key to understanding bone tissue. It helps in the exchange of nutrients and waste. This is vital for bone health.
Definition and Basic Function
Volkmann’s Canal is a perforating canal. It connects Haversian canals. This allows blood vessels and nerves to pass through compact bone.
Its main job is to keep bone tissue healthy and working well. The canals are a big part of the bone’s structure. They help keep the skeletal system healthy.
Historical Discovery and Naming
Alfred Volkmann, a German physiologist, named Volkmann’s Canal. He was a big name in bone anatomy. His work helped us understand bones better.
Richard von Volkmann’s Contributions
Richard von Volkmann was also important in anatomy. He made big contributions, even though the canals are named after Alfred Volkmann.
Evolution of Understanding
Our knowledge of Volkmann’s Canal has grown over time. New discoveries in microscopic anatomy have shown its importance. It’s key for bone health and microcirculation.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Perforating canal connecting Haversian canals |
| Basic Function | Pathway for vascular and nervous supply |
| Named After | Alfred Volkmann |
The Microscopic Structure of Bone
Understanding bone’s microscopic structure is key to knowing how it works and stays strong. Bone tissue mainly has two types: compact bone and cancellous bone.
Compact vs. Cancellous Bone
Compact bone, or cortical bone, is the dense outer layer of bone. Cancellous bone, on the other hand, is the spongy, porous tissue inside the bone.
Structural Differences
Compact bone is made up of osteons, the basic building blocks. These osteons are arranged around a central canal, called the Haversian canal. Cancellous bone, without osteons, has a network of trabeculae instead.
Functional Implications
The differences in structure between compact and cancellous bone are important. Compact bone gives strength and support. Cancellous bone helps reduce weight and increases surface area for metabolic activities.
The Hierarchical Organization of Bone Tissue
Bone tissue is organized in a hierarchical way, from cells to tissues.
Cellular Level Organization
At the cellular level, bone tissue includes osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts. These cells work together to keep bone healthy and to remodel it.
Tissue Level Architecture
At the tissue level, the arrangement of collagen fibers and mineralized matrix gives bone its strength and elasticity.
Anatomical Location of Volkmann’s Canal
It’s important to know where Volkmann’s Canal is in the body. It’s found in the cortical bones. These canals help connect Haversian canals to the periosteum. This connection is key for nutrient and waste exchange.
Distribution Throughout the Skeletal System
Volkmann’s Canals are found in many bones. They are seen in both long bones and flat or irregular bones.
Long Bones
In long bones, Volkmann’s Canals run perpendicular to Haversian canals. This setup helps with nutrient and waste exchange between the periosteum and bone marrow. It’s vital for the bones’ strength and function.
Flat and Irregular Bones
Flat and irregular bones also have Volkmann’s Canals. These canals help with blood supply and bone health. They aid in exchanging nutrients and waste.
Density and Orientation Patterns
The density and direction of Volkmann’s Canals change in different bone areas. These changes reflect the bone’s adaptation to its environment.
Regional Variations
The density of Volkmann’s Canals changes based on the bone’s stress levels. Areas under more stress have denser canals. This helps keep the bone healthy and strong.
Functional Adaptations
The direction and density of Volkmann’s Canals vary based on the bone’s needs. This variation is key for the bone’s health and function.
| Bone Type | Density of Volkmann’s Canals | Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Long Bones | High | Perpendicular to Haversian canals |
| Flat Bones | Moderate | Variable |
| Irregular Bones | Variable | Adapted to local anatomy |
The Structure of Volkmann’s Canal
Understanding Volkmann’s Canal is key to knowing its role in bone tissue. These canals connect Haversian canals, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, oxygen, and waste.
Microscopic Anatomy
The microscopic look at Volkmann’s Canal shows its detailed structure. These canals are not random; they have specific sizes and shapes for their job.
Dimensions and Morphology
Volkmann’s Canals come in different sizes, from 20 to 100 micrometers. Their shape is designed for their role, often being more complex than Haversian canals.
Structural Components
The parts of Volkmann’s Canals include the lumen, which has blood vessels and nerves. These parts are vital for the canal’s work, giving bone cells the nutrients and support they need.
“Volkmann’s canals contain blood vessels and nerves that provide nutrition and support to bone cells,” highlighting their importance in bone health.
Cellular Components
Volkmann’s Canals have a variety of cells, both permanent and temporary.
Resident Cells
Cells like osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts live near Volkmann’s Canals. They are key for bone repair and upkeep.
Transient Cellular Elements
Cells like immune cells can also be found in the canals. They are more present during inflammation or when the bone is healing.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Osteocytes | Maintain bone matrix, respond to mechanical stress |
| Osteoblasts | Form bone matrix, mineralize bone |
| Osteoclasts | Resorb bone tissue, critical for remodeling |
Volkmann’s Canal vs. Haversian Canal
It’s important to know the difference between Volkmann’s Canal and Haversian Canal to understand bone anatomy. Both are key to the bone’s structure but do different jobs and have unique features.
Key Structural Differences
The main difference is how they are arranged in the bone. Volkmann’s Canals go across the bone, linking Haversian canals. They help move nutrients and waste around.
Orientation and Organization
Haversian canals, by contrast, run along the bone’s length. This setup creates a network that helps keep the bone strong.
Size and Distribution
The size and how they spread out differ too. Volkmann’s Canals are not all the same size and spread out in a random way. Haversian canals are more alike in size and follow a regular pattern.
Functional Relationships
Volkmann’s Canal and Haversian Canal work together. They both play important roles in the bone’s environment.
Complementary Roles
Volkmann’s Canals link different Haversian systems. This lets them share nutrients, waste, and signals. It’s key for keeping the bone healthy and helping it change shape.
Integrated Network Functions
Together, they make a network that meets the bone’s needs. As a leading researcher said,
“The complex network of Volkmann’s and Haversian canals shows how organized and complex bone tissue is.”
The Role of Volkmann’s Canal in the Osteon System
Volkmann’s Canal is key in the osteon system. It helps with bone remodeling and nutrient supply. This part of the bone’s structure is vital for its health and function.
Integration with Haversian Systems
Volkmann’s Canals link Haversian canals to the periosteum. This connection is important for nutrient and waste exchange. It keeps bone tissue healthy.
Structural Connectivity
Volkmann’s Canals connect Haversian canals, improving bone’s vascular supply. This is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients.
Functional Integration
Volkmann’s Canals work with Haversian systems to distribute nutrients evenly. This is important for keeping osteocytes healthy.
Contribution to Bone Microarchitecture
Volkmann’s Canals are important for bone microarchitecture. They influence bone’s mechanical properties and remodeling.
Mechanical Properties
Volkmann’s Canals help distribute stress, reducing fracture risk. They play a role in bone’s mechanical strength.
Adaptive Remodeling
Volkmann’s Canals help in bone remodeling. They allow for communication between osteoclasts and osteoblasts. This helps the bone adapt to changes.
| Feature | Haversian Canal | Volkmann’s Canal |
|---|---|---|
| Orientation | Longitudinal | Transverse |
| Function | Nutrient Supply | Transverse Communication |
| Connection | Connected by Volkmann’s Canals | Connects Haversian Canals |
Physiological Functions of Volkmann’s Canal
Volkmann’s Canal is a complex network that supports many important functions for bone health. It helps exchange nutrients and waste between bone and surrounding tissues. This is key to keeping bones strong and healthy.
Nutrient Transport Mechanisms
Nutrient transport is a major role of Volkmann’s Canal. It ensures bone cells get the nutrients they need to survive and work well. This includes oxygen, glucose, and minerals for bone growth.
Oxygen and Glucose Delivery
Oxygen and glucose are essential for bone cells’ metabolic processes. Volkmann’s Canal connects with blood vessels to deliver these nutrients. An orthopedic specialist notes,
“The vascular supply through Volkmann’s Canal is critical for maintaining the metabolic activity of bone cells.”
Mineral Transport
Minerals like calcium and phosphate are moved through Volkmann’s Canal. They help mineralize bone tissue, keeping bones dense and strong. Mineral transport mechanisms are vital to Volkmann’s Canal’s functions.
Waste Removal Processes
Volkmann’s Canal also helps remove waste from bone tissue. This includes clearing metabolic waste and cellular debris.
Metabolic Waste Clearance
Clearing metabolic waste is key for bone cell health. Volkmann’s Canal provides a way for waste to be removed from bone. Efficient metabolic waste clearance prevents toxic buildup.
Cellular Debris Elimination
Cellular debris from bone remodeling is removed through Volkmann’s Canal. This keeps bone tissue healthy and functional. Eliminating cellular debris is a critical function of Volkmann’s Canal.
Vascular Supply Through Volkmann’s Canal
Understanding how Volkmann’s Canal supplies blood to bones is key to knowing bone health. This canal has blood vessels that feed the bone, keeping it nourished and healthy.
Blood Vessel Organization
The blood vessels in Volkmann’s Canal are organized in a complex way. Arterioles carry oxygen-rich blood to the bone. On the other hand, venules take away blood that’s low in oxygen.
Arteriolar Components
Arteriolar parts in Volkmann’s Canal are vital for bringing oxygen and nutrients to bone cells. These small arteries split into capillaries. Capillaries help exchange substances between blood and bone tissue.
Venous Drainage
Venous drainage is also key, as it removes waste from the bone. The venules in Volkmann’s Canal collect blood that’s low in oxygen and waste. This keeps the bone healthy.
Microcirculation Patterns
Microcirculation in Volkmann’s Canal involves the flow of blood. Blood flow dynamics and regulatory mechanisms work together to keep circulation optimal.
Blood Flow Dynamics
Blood flow in Volkmann’s Canal is influenced by blood pressure and vessel resistance. This flow ensures the bone gets the nutrients and oxygen it needs.
Regulatory Mechanisms
Regulatory mechanisms like vasodilation and vasoconstriction control blood flow. These mechanisms adjust nutrient and oxygen supply to meet bone tissue needs.
Neural Components of Volkmann’s Canal
Volkmann’s Canal is complex because of its neural parts. It has nerve fibers that help with sensory and autonomic innervation. This is key for bone health.
Innervation Patterns
The innervation patterns in Volkmann’s Canal vary. It includes different types of nerve fibers.
Nerve Fiber Types
There are myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. Each type has its own role.
Distribution Networks
The nerve fibers spread out in complex ways. This ensures the bone is fully innervated.
Sensory and Autonomic Functions
The nerve fibers in Volkmann’s Canal handle sensory and autonomic functions.
Nociceptive Signaling
Nociceptive signaling is key for pain detection. It helps us respond to injuries or diseases.
Vasomotor Control
Vasomotor control manages blood flow. It’s vital for bone health and function.
Volkmann’s Canal and Cortical Bone Interaction
Volkmann’s Canal is key in how it works with cortical bone. It changes the bone’s porosity and how it works mechanically. This is important for understanding bone health and diseases.
Structural Integration
The way Volkmann’s Canal and cortical bone work together is complex. Penetration patterns show how the canals go through the bone. This creates paths for blood and nerves.
Penetration Patterns
Volkmann’s Canals go through the bone at different angles. This creates a network that helps keep the bone alive. It’s important for getting nutrients and oxygen to bone cells.
Interface Characteristics
The area where Volkmann’s Canals meet cortical bone is complex. It involves cells and matrix working together. This area is key for keeping the bone healthy and helping it repair.
| Characteristics | Description | Impact on Bone |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration Angle | Varied angles of penetration | Affects nutrient supply |
| Interface Complexity | Complex cellular and matrix interplay | Influences bone homeostasis |
Functional Significance
The role of Volkmann’s Canal and cortical bone interaction is big. It affects how porous the bone is and its mechanical strength. Cortical porosity is linked to bone density and strength. The bone’s ability to handle stress is also impacted.
Cortical Porosity Impact
The connection between Volkmann’s Canal and cortical bone affects bone density. Reduced cortical porosity means stronger bones. This is because denser bones are less likely to break.
Biomechanical Implications
The biomechanical effects of Volkmann’s Canal and cortical bone interaction are significant. They impact the bone’s ability to handle stress. Biomechanical properties like stiffness and toughness are influenced by this interaction.
“The relationship between Volkmann’s Canals and cortical bone shows how complex bone architecture is. It’s vital for bone health.”
The Role of Volkmann’s Canal in Bone Remodeling
Volkmann’s Canal is key in bone remodeling. It helps cells move and nutrients get where they need to go. This process involves osteoclasts and osteoblasts working together.
Osteoclast and Osteoblast Activity
Osteoclasts break down bone, while osteoblasts build new bone. Their work keeps bones healthy. Volkmann’s Canal helps them do their jobs.
Cellular Migration Pathways
Volkmann’s Canal lets osteoclasts and osteoblasts move around. This helps them reach where they need to be. It connects Haversian systems for cell and nutrient exchange.
Activation Mechanisms
Signaling pathways turn osteoclasts and osteoblasts on. Volkmann’s Canal makes sure they get the right signals and nutrients.
Remodeling Signaling Pathways
Bone remodeling is controlled by complex signals. These signals involve molecular mediators that help osteoclasts and osteoblasts work together.
Molecular Mediators
RANKL and OPG are important for osteoclasts. The right balance between them is key for bone health.
Temporal Sequence of Events
Bone remodeling starts with osteoclasts breaking down bone. Then, osteoblasts build new bone. Volkmann’s Canal helps by providing a path for cells and nutrients.
In summary, Volkmann’s Canal is essential for bone remodeling. It helps osteoclasts and osteoblasts work and provides a way for cells and nutrients to move.
Developmental Aspects of Volkmann’s Canal
Learning about Volkmann’s Canal helps us understand bone health. It’s key for blood flow and talking between bone cells.
Formation During Embryonic Development
Volkmann’s Canal starts forming in embryonic development. This is a key time for the bones to grow.
Temporal Sequence
The canal forms in a certain order. This order is important for it to fit right in the bone.
Molecular Regulation
Many growth factors and signals help it form. Molecular signals guide its growth, shaping its structure and function.
Changes Throughout the Lifespan
Volkmann’s Canal changes as we grow older. It adapts to the bone’s needs.
Childhood and Adolescence
In childhood and adolescence, it grows and gets better. It’s important for bone growth and fixing bones.
Aging-Related Alterations
With age, it might change in ways that affect bone health. Knowing these changes helps fight bone diseases as we get older.
Imaging Techniques for Visualizing Volkmann’s Canal
Imaging techniques are key in studying Volkmann’s Canal. They help us see its structure and function in detail. Many methods are used to look at this complex network in the bone.
Microscopy Methods
Microscopy is a basic tool for looking at Volkmann’s Canal’s tiny details. Different microscopy methods give us different views of its structure.
Light Microscopy Approaches
Light microscopy is often used first to look at Volkmann’s Canal. It shows us the big picture of its shape and how it fits with the bone around it.
Electron Microscopy Applications
Electron microscopy is used for even more detailed images. It lets us see the canal’s surface and its tiny parts up close.
Advanced Imaging Technologies
There are also new imaging technologies for looking at Volkmann’s Canal.
Micro-CT Analysis
Micro-CT analysis is great for making 3D pictures of Volkmann’s Canal. It gives us detailed info on its shape and how it connects with the bone.
Emerging Visualization Methods
New methods like synchrotron imaging are being looked into. They might help us learn even more about Volkmann’s Canal’s structure and function.
Using these imaging techniques together has really helped us understand Volkmann’s Canal better. By combining old and new methods, researchers can see the whole picture of this important part of bone anatomy.
Pathological Conditions Affecting Volkmann’s Canal
Volkmann’s Canal is a key part of bone anatomy. It can be affected by many diseases. These diseases can change how the canal works and cause problems.
Bone Diseases and Their Impact
Diseases like osteoporosis and metabolic bone disorders can harm Volkmann’s Canal. These conditions can weaken the canal and change its structure.
Osteoporosis Effects
Osteoporosis makes bones weaker and more prone to fractures. It can also damage Volkmann’s Canal. This weakens bone health and makes bones more vulnerable to disease.
Metabolic Bone Disorders
Conditions like Paget’s disease can also affect Volkmann’s Canal. These diseases can cause bones to grow abnormally. This can harm the canal’s function.
Trauma and Healing Processes
Bone trauma can also affect Volkmann’s Canal. It can disrupt its function and make healing harder.
Fracture Repair Involvement
Volkmann’s Canal is important for bone healing. It helps bring nutrients and cells needed for repair. Damage to the canal can slow healing.
Ischemic Complications
Ischemia can happen when trauma cuts off blood supply to the bone. This can harm Volkmann’s Canal and cause more damage or even bone death.
| Pathological Condition | Effect on Volkmann’s Canal | Consequence for Bone Health |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Compromised integrity | Increased fracture risk |
| Metabolic Bone Disorders | Abnormal bone remodeling | Deformed bones |
| Trauma | Disrupted function | Impaired healing |
In conclusion, Volkmann’s Canal is affected by many diseases and trauma. Understanding these effects is key to understanding bone health. Keeping Volkmann’s Canal healthy is vital.
Clinical Significance of Volkmann’s Canal
Volkmann’s Canal is very important in orthopedic conditions. It helps with blood flow and bone repair. This makes it key in understanding bone diseases.
Relevance in Orthopedic Conditions
Volkmann’s Canal is vital for diagnosing and treating orthopedic issues. It ensures bones get the blood they need to stay healthy.
Diagnostic Implications
Having Volkmann’s Canal in good shape is important for diagnosing bone problems. Doctors use special imaging to check its condition.
Treatment Considerations
Knowing about Volkmann’s Canal helps doctors plan better treatments. This knowledge helps in surgeries and other treatments.
Implications for Bone Health
The health of Volkmann’s Canal affects bone health. Problems with the canal can lead to weaker bones.
Preventative Strategies
Keeping Volkmann’s Canal healthy is good for bones. Making lifestyle choices that help bone density is important.
Therapeutic Targets
Volkmann’s Canal could be a target for treating bone diseases. Studying its role in bone health might lead to new treatments.
| Aspect | Relevance to Orthopedic Conditions | Implications for Bone Health |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Implications | Advanced imaging for visualization | Assessment of canal integrity |
| Treatment Considerations | Guiding surgical interventions | Influencing therapeutic strategies |
| Preventative Strategies | Lifestyle choices and interventions | Preserving bone density |
Current Research on Volkmann’s Canal
Volkmann’s Canal is a key part of the bone system. Scientists are studying it to learn more about bone health and diseases. They are looking into its role and structure.
Recent Scientific Discoveries
Recent studies have made big progress in understanding Volkmann’s Canal. Functional insights have shown its importance in moving nutrients and waste.
Functional Insights
Researchers have focused on how the canal helps exchange nutrients and waste with the bloodstream. This is a major area of study.
Structural Revelations
New imaging methods have shown more about Volkmann’s Canal’s structure. They have found details about its links with Haversian canals.
Future Research Directions
Research on Volkmann’s Canal is ongoing, leading to new paths to explore. Technological advances in imaging and analysis will be key in future studies.
Technological Advances
Better microscopy and imaging will help study Volkmann’s Canal in more detail. This could uncover new information about its structure and function.
Therapeutic Applications
Learning more about Volkmann’s Canal could lead to new treatments for bone diseases. This includes conditions like osteoporosis.
Conclusion
Volkmann’s Canal is key to bone health. It helps blood vessels and nerves reach the bone. This is vital for the bone’s function and health.
The network of Volkmann’s Canals and Haversian canals is called the osteon system. It’s essential for keeping bones strong.
Learning about Volkmann’s Canal helps us understand bone remodeling. This is how bones stay healthy and strong.
Studies on Volkmann’s Canal have shown its importance in bone diseases. More research will give us even more insights into bone health.
In short, Volkmann’s Canal is a vital part of bone anatomy. Studying it helps us better understand and treat bone diseases. This is important for keeping bones healthy.