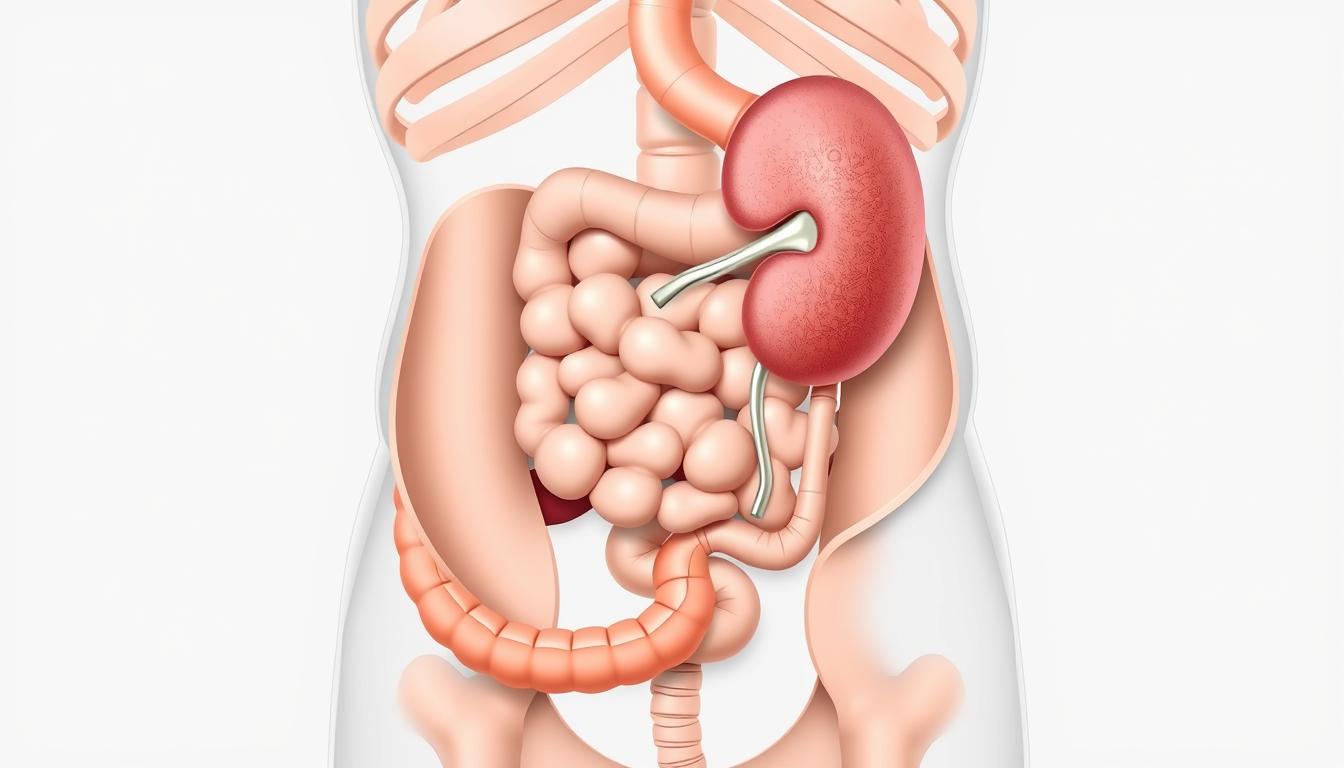
The left hypochondriac region is a complex area. It houses vital organs like parts of the stomach, the top of the left lobe of the liver, the left kidney, the spleen, and the tail of the pancreas.
It’s important for doctors and students to understand these organs and how they work together. Computer science and information technology have changed how we study anatomy. These tools help us learn more about how organs in the left hypochondriac region function and interact.
Using Technical Informatics in medicine helps us diagnose and treat better. This leads to better health outcomes for patients.
Anatomical Overview of the Left Hypochondriac Region
To understand the left hypochondriac region, you need to know its anatomy and why it’s important. It’s under the ribcage and has parts of the spleen, stomach, and pancreas.
Definition and Boundaries
The left hypochondriac region is the space under the left lower ribs. It’s bordered by the diaphragm above, the ribcage on the sides, and the left midclavicular line in the middle. This area is key because it holds important organs like the spleen and parts of the stomach.
Clinical Significance
The left hypochondriac region is important for health because it has vital organs. The spleen helps the immune system, and the stomach is vital for digestion. Knowing this area well is essential for diagnosing and treating problems.
Digital Mapping Applications
New digital systems and information technology have made detailed maps of the left hypochondriac region possible. These tools help doctors locate and study this area accurately. They use data analysis to help make better diagnoses and treatments.
The Spleen: Structure and Function
The spleen is a key part of our immune system. It filters blood and stores red blood cells in the left side of the body. Its structure and function are vital for our health.
Anatomical Characteristics
The spleen is in the upper left part of the abdomen, under the rib cage. It has a protective capsule. The spleen has white pulp for immune responses and red pulp for blood filtering.
Physiological Roles
The spleen filters blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells. It also stores red blood cells and lymphocytes, helping fight infections. This makes the spleen key for our immune system.
Digital Modeling of Splenic Function
Thanks to computer science and software engineering, we have digital models of the spleen. These models help us understand the spleen’s role in health and disease.
Computational Fluid Dynamics
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models blood flow in the spleen. CFD simulations help researchers understand how the spleen filters blood and how it’s affected by conditions.
Cellular Automation Models
Cellular automation models simulate spleen cell behavior. These models help predict how the spleen responds to diseases. They aid in finding new treatments.
| Modeling Technique | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Computational Fluid Dynamics | Simulates blood flow | Enhances understanding of splenic filtration |
| Cellular Automation Models | Simulates cellular behavior | Aids in predicting splenic response to disease |
Using programming languages like Python and MATLAB in these models has made complex simulations easier. This has deepened our understanding of the spleen and its role in health.
The Stomach: Upper Left Portion
The stomach’s upper left part is in the left hypochondriac region. It’s key to the digestive system. This area is important for its shape and how it works.
Anatomical Position in the Left Hypochondrium
The stomach is in the upper left part of the abdomen. Its upper left part is in the left hypochondriac region. This spot is vital for digestion and working with other organs.
Functional Aspects
The stomach’s main job is to break down food into smaller bits. The upper left part of the stomach does this. It uses its muscles to mix food with stomach juices.
Data Analysis in Gastric Motility Studies
Understanding how the stomach moves is key for treating stomach problems. Data analysis is important for studying stomach movement.
Sensor Technologies
Advanced sensors track stomach movement. They can see when the stomach muscles contract and how food moves.
Signal Processing Algorithms
Algorithms are used to make sense of the data from sensors. They help spot normal and abnormal stomach movements. This helps doctors plan treatments.
By using sensors and algorithms, experts can learn more about stomach movement. This helps us understand digestive health better.
The Left Lobe of the Liver
The left lobe of the liver is in the left side of the belly. It’s key for liver function. The liver cleanses the blood, breaks down food, and makes important chemicals for digestion.
Anatomical Extension into Left Hypochondrium
The left lobe of the liver is important because it reaches into the left side of the belly. Knowing this helps us understand how organs in the belly work together.
Functional Significance
The left lobe, like the rest of the liver, helps with detoxification and metabolic processes. It’s vital for keeping the liver healthy.
Software Solutions for Liver Function Assessment
New tech in software engineering and information technology has improved liver function tests. These include:
- Elastography analysis for evaluating liver stiffness.
- Perfusion quantification to assess liver blood flow.
Elastography Analysis
Elastography is a non-invasive way to check liver stiffness, which shows liver fibrosis. It uses digital systems for precise measurements.
Perfusion Quantification
Perfusion quantification looks at blood flow to the liver. It’s key for understanding liver health and spotting problems. This is done with advanced imaging techniques and smart software.
The Tail of the Pancreas
The pancreas’s tail is in the left hypochondriac area. It’s key for both making hormones and digestive enzymes. It stretches towards the spleen.
Anatomical Position
The tail of the pancreas is in the left hypochondriac region, near the splenic hilum. It connects to the pancreatic body and tapers towards the spleen.
Endocrine and Exocrine Functions
The tail of the pancreas has both endocrine and exocrine roles. It makes hormones like insulin and glucagon for glucose control. It also produces digestive enzymes for food breakdown.
Information Technology in Pancreatic Imaging
New tech in information technology has boosted pancreatic imaging. CT scans and MRI get clearer thanks to algorithms.
Contrast Enhancement Algorithms
Contrast enhancement algorithms are vital for clear pancreatic images. They help see the pancreas and any issues better.
Automated Lesion Detection
Automated lesion detection uses computer science and data analysis. It spots pancreatic problems fast and accurately. This tech could change how we diagnose pancreatic diseases.
Information technology has changed how we diagnose and treat pancreatic issues. As tech gets better, we’ll have even more precise tools.
The Left Kidney: Upper Pole
The left kidney’s upper pole is a key part of the kidney found in the left hypochondriac region. Its location is important for understanding how it works and its role in health.
Anatomical Relationship to Left Hypochondrium
The upper pole of the left kidney is in the left hypochondriac region. This area is protected by the rib cage. It’s also where the kidney’s blood vessels and ureter connect.
Functional Aspects
The left kidney, including its upper pole, filters waste from the blood. It helps control blood pressure and keeps electrolyte levels balanced. These tasks are essential for good health, and problems can cause serious issues.
Digital Systems for Renal Function Assessment
Modern medicine uses digital systems to check kidney function. These include:
- Advanced imaging techniques
- Software solutions for data analysis
- Applications of software engineering in medical diagnostics
Glomerular Filtration Rate Calculators
The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) calculator is a key tool. It estimates how well the kidneys filter waste from the blood.
3D Reconstruction of Renal Vasculature
3D reconstruction techniques show the kidney’s blood vessels in detail. This helps doctors diagnose and plan surgeries. It makes kidney assessments more precise.
Healthcare professionals use these digital systems and data analysis to understand kidney function better. This helps them diagnose problems more effectively.
The Splenic Flexure of the Colon
The splenic flexure is in the upper left part of the abdomen. It’s a key bend in the large intestine. It marks where the transverse colon meets the descending colon.
Anatomical Position
The splenic flexure is near the spleen in the left hypochondriac region. It’s located close to the 10th and 11th ribs. Knowing its exact spot is important for medical procedures.
Functional Significance
The splenic flexure is more than just a landmark. It affects how the colon works. It’s a common place for gas and can be involved in diseases like diverticulitis and tumors. Its location and how it moves can also affect the flow of contents in the colon.
Virtual Colonoscopy Technology
Virtual colonoscopy is a new, non-invasive way to see the colon. It uses computer science and IT to make detailed images from CT scans. This technology is made possible by advanced programming languages and algorithms.
Image Segmentation Techniques
Image segmentation is key in virtual colonoscopy. It uses complex algorithms to separate different tissues and structures in the colon. This step is vital for spotting problems and needs a lot of computing power.
Computer-Aided Detection Systems
Computer-aided detection (CAD) systems help find polyps and other lesions during virtual colonoscopy. They use machine learning and pattern recognition to point out possible issues. This helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses.
Computer science and medical imaging have changed how we look at the splenic flexure and the colon. Virtual colonoscopy is a big step forward in diagnosis. It’s a less invasive way to check the colon compared to traditional methods.
Vascular Supply to the Left Hypochondriac Region
Understanding the blood flow to the left hypochondriac region is key for diagnosing and treating health issues. This area is home to important organs like the spleen, stomach, and parts of the liver and pancreas. It gets its blood supply from a network of arteries and veins.
Arterial Supply
The blood to the left hypochondriac region comes mainly from the aorta and its main branches. The splenic artery, a branch of the celiac trunk, feeds the spleen. The left gastric artery and short gastric arteries supply blood to the stomach. The left lobe of the liver gets its blood from the left hepatic artery.
Venous Drainage
The venous drainage of the left hypochondriac region mirrors the arterial supply. The splenic vein drains the spleen and parts of the stomach and pancreas. It merges with the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein. The left gastric vein and short gastric veins also drain into the portal vein, aiding the hepatic portal system.
Computational Modeling of Regional Blood Flow
Technical informatics has led to advanced blood flow modeling in the left hypochondriac region. Methods like finite element analysis and machine learning applications are being used more often.
Finite Element Analysis
Finite Element Analysis (FEA) simulates complex systems under different conditions. In vascular supply, FEA models blood flow and pressure in arteries and veins. It offers insights into vascular diseases.
Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning algorithms work on large vascular supply and blood flow datasets. They enable predictive analytics and personalized medicine. These tools help in early disease detection and treatment planning.
| Technique | Application | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Finite Element Analysis | Modeling blood flow and pressure | Insights into vascular pathologies |
| Machine Learning | Predictive analytics | Early detection and personalized treatment |
Technical Informatics in Anatomical Imaging
Technical informatics has greatly improved the accuracy of anatomical imaging. It combines computer science and information technology. This field is key in creating and using imaging technologies.
CT Scanning Technology
Computed Tomography (CT) scanning is a vital tool for doctors. CT scanners combine X-ray measurements from different angles. This creates detailed images of the body’s inside.
Thanks to reconstruction algorithms and detector technology, images are clearer. And they use less radiation.
MRI Applications
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) also benefits from technical informatics. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves. It creates detailed images of organs and tissues.
Technical informatics improves MRI with better image reconstruction techniques and pulse sequence design. This makes seeing body structures clearer.
Programming Languages in Medical Image Processing
Programming languages like Python and C++ are used in medical image processing. Python is popular for its ease and libraries for image analysis and machine learning. C++ is used for fast and efficient computing tasks.
Python for Image Analysis
Python’s OpenCV and scikit-image libraries offer powerful tools for image analysis. They help developers do complex tasks like segmentation and feature extraction well.
C++ in High-Performance Computing
C++ is great for tasks that need fast processing, like real-time image processing and 3D reconstruction. Its speed makes it perfect for tough tasks in medical imaging.
DICOM Standards and Implementation
The DICOM standard is key for sharing medical imaging data. Technical informatics makes sure systems follow DICOM standards. This helps different devices and systems work together.
In summary, technical informatics is essential for improving anatomical imaging, like CT and MRI. Using programming languages like Python and C++ and following DICOM standards shows its importance.
Artificial Intelligence Applications in Organ Assessment
AI has made big strides in medical imaging, like organ segmentation and finding diseases. This makes organ checks more accurate and faster.
Deep Learning for Organ Segmentation
Deep learning is now key for cutting out organs in medical pictures. It helps draw clear lines around organs like the spleen and liver. This is vital for doctors to make diagnoses and plan treatments.
Convolutional Neural Networks in Pathology Detection
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are great at spotting diseases in medical images. They look for patterns and oddities. This helps doctors find diseases early, like those in the left side of the body.
Natural Language Processing for Radiology Reports
Natural Language Processing (NLP) helps read radiology reports better. It uses:
Text Mining Techniques
Text mining digs out important data from reports. It finds trends and patterns that help doctors make better choices.
Automated Report Generation
NLP also makes radiology reports automatically. This cuts down on radiologists’ work and makes reports more consistent.
| AI Application | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Deep Learning | Organ Segmentation | Precise delineation of organs |
| CNNs | Pathology Detection | Early disease detection |
| NLP | Radiology Report Analysis | Improved information extraction |
Software Engineering in Medical Visualization
Medical visualization has made big strides thanks to software engineering. It has led to more precise and detailed visualizations.
3D Rendering Algorithms
Software engineering has greatly impacted 3D rendering algorithms. These algorithms are key for making detailed 3D models from medical scans like MRI and CT.
Advanced 3D rendering algorithms bring many benefits. They include:
- Enhanced visualization of complex structures
- Improved diagnostic accuracy
- Better preoperative planning
Augmented Reality Applications
Augmented reality (AR) has also been a big help in medical visualization. AR adds digital info to the real world, making medical data easier to understand.
AR in medical visualization offers several advantages. These include:
- Enhanced patient education through interactive visuals
- Improved surgical precision with real-time data
- Increased accuracy in diagnostics
User Interface Design for Medical Software
User interface design is key for making medical software easy to use. It aims to create interfaces that are both intuitive and ergonomic.
Ergonomic Considerations
Ergonomic design makes sure the software is comfortable to use for long times. This reduces fatigue and errors.
Workflow Optimization
Optimizing the workflow in medical software boosts productivity. It involves making processes smoother and cutting out unnecessary steps.
By focusing on these areas, software engineering helps create better and easier-to-use medical visualization tools.
Network Security in Medical Imaging Systems
Medical imaging systems need strong network security to keep patient data safe. These systems handle very sensitive information, making them a prime target for hackers.
HIPAA Compliance in Digital Systems
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) has strict rules for protecting patient health info. Medical imaging systems must follow these rules to keep patient data safe and secure.
- Implementing access controls and encryption
- Conducting regular security audits
- Training personnel on HIPAA compliance
Secure Transmission Protocols
It’s vital to use secure ways to send patient data. SSL/TLS and IPSec are technologies that help keep data safe while it’s being sent.
Blockchain Applications in Medical Data Integrity
Blockchain technology is a great way to make medical data more secure. It uses a shared ledger to keep medical images and patient data safe and open to all.
Smart Contracts for Data Access
Smart contracts can help control who gets to see sensitive info. They make sure only the right people can access important data.
Distributed Ledger Benefits
Using a distributed ledger brings many advantages. It makes data more secure, proves where data comes from, and makes everything more transparent.
| Security Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Access Controls | Limiting access to authorized personnel | Enhanced security |
| Encryption | Protecting data from unauthorized access | Data confidentiality |
| Blockchain | Ensuring data integrity and transparency | Tamper-proof data |
Data Analysis in Left Hypochondriac Pathologies
Data analysis is key to understanding left hypochondriac pathologies. It uses various methods to look into disease rates, treatment success, and trends. This helps healthcare experts make better decisions.
Statistical Methods in Disease Prevalence
Statistical methods are important for knowing disease rates in the left hypochondriac area. They analyze big data to spot patterns and trends. This helps doctors in their work.
Predictive Analytics for Treatment Outcomes
Predictive analytics helps guess how well treatments will work for left hypochondriac diseases. It uses old data and machine learning to guide doctors.
Big Data Approaches to Epidemiology
Big data changes how we study diseases in the left hypochondriac area. It uses lots of data and new methods to understand disease better.
Data Mining Techniques
Data mining finds patterns in big data about left hypochondriac diseases. It helps find high-risk patients and improve care plans.
Visualization Tools
Visualization tools make complex data easy to understand. They help share findings with everyone, supporting better decisions.
In summary, data analysis is vital for managing left hypochondriac pathologies. It uses stats, predictive analytics, and big data to help patients and grow technical informatics.
Conclusion: The Intersection of Anatomy and Technical Informatics
The mix of anatomy and technical informatics has changed how we see the human body. It’s focused on the complex parts in the left hypochondriac area. Thanks to computer science and information technology, we now have better imaging and data analysis. This has made healthcare better and helped patients more.
Technical informatics has made it easier to see and check organs like the spleen, stomach, and liver’s left lobe. Computer science helps create smart algorithms for handling images. Information technology keeps medical data safe and lets it move easily.
As we keep moving forward, the blend of anatomy and technical informatics will be key in medical care’s future. With these tools, doctors can get better at diagnosing, plan treatments more effectively, and care for patients better.