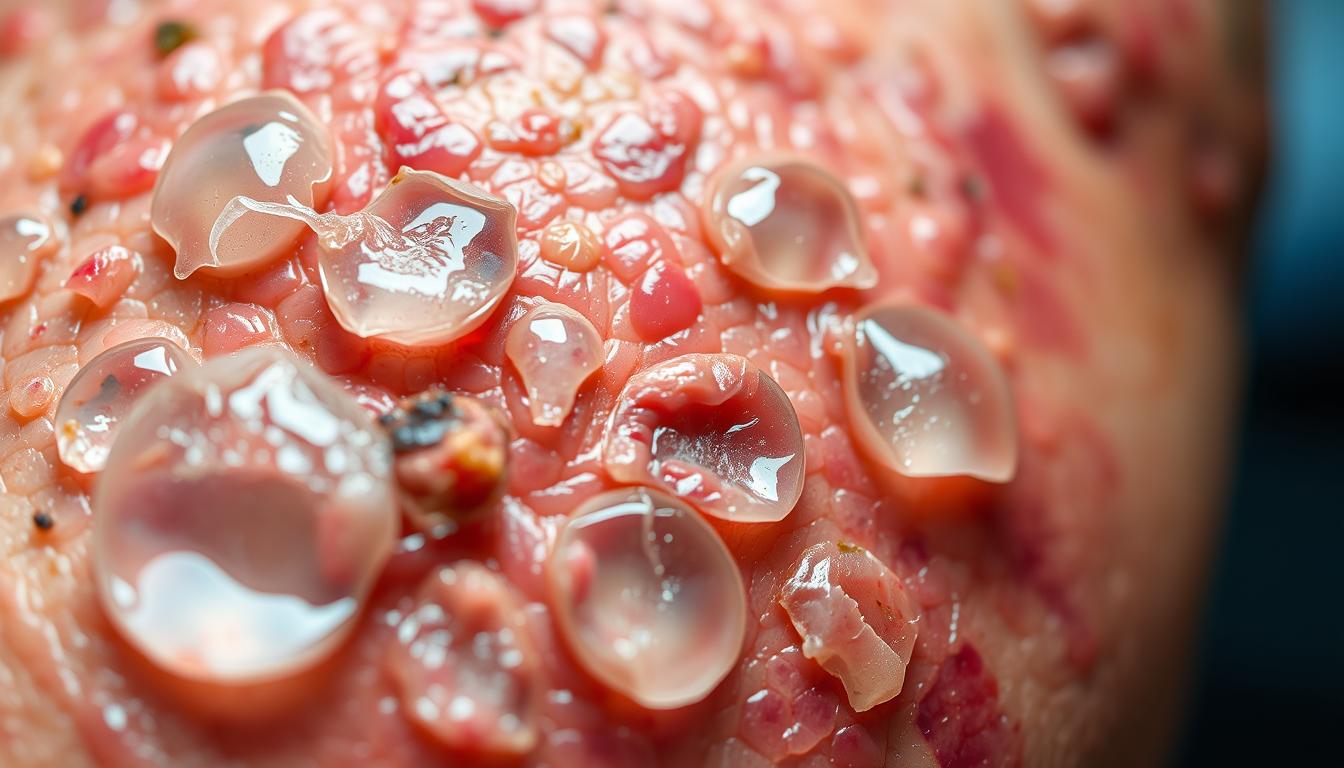
Fracture blisters on the skin are a serious sign that needs quick action. They show up after a traumatic injury and tell us how bad the injury is.
It’s key for doctors to understand the importance of these blisters. They can make treatment harder and change how well a patient does.
Looking at a photo of fracture blisters helps doctors learn more. This helps them decide the best care for their patients.
What Are Fracture Blisters: Definition and Clinical Significance
Fracture blisters are a key issue in orthopedic trauma. They need a detailed look at their features and how they affect patient care. These blisters are a major problem that can happen from severe injuries, like fractures.
Medical Definition and Characteristics
Fracture blisters are blisters that form on the skin over a fracture. They can be clear or filled with blood. The symptoms of fracture blisters include pain, swelling, and trouble moving the affected limb.
Prevalence in Orthopedic Trauma
Fracture blisters are common in orthopedic trauma, often seen in the ankle, elbow, and distal tibia. Research shows they happen in many patients with certain fractures. This makes them very important in medical care.
Impact on Patient Care
Fracture blisters can make patient care harder, affecting surgery and wound care. Knowing the causes of fracture blisters is key to treating them well.
These blisters can harm patient outcomes, like increasing infection risk and healing time. So, doctors need to understand fracture blisters well to help patients with orthopedic trauma.
The Pathophysiology Behind Fracture Blisters
To understand fracture blisters, we need to look at how they form and their link to bone injuries. These blisters are a big problem after severe fractures. They can slow down healing and cause more fracture blister complications.
Mechanism of Formation
Fracture blisters happen when the skin and tissues under it get damaged by a fracture. This damage causes fluid to build up, creating blisters. How bad the fracture is and the damage to soft tissues affect how likely blisters are to form.
Relationship to Underlying Bone Injury
The severity of the bone injury is linked to the chance of getting fracture blisters. More serious fractures damage soft tissues more, raising the risk of blisters. The table below shows how fracture severity relates to blister incidence.
| Fracture Severity | Incidence of Fracture Blisters |
|---|---|
| Mild | Low |
| Moderate | Moderate |
| Severe | High |
Tissue Edema and Compartment Pressure
Tissue swelling and high compartment pressure are key in making fracture blisters. Swelling comes from the body’s reaction to the fracture, making pressure in the fascial compartments go up. This pressure can cut off blood flow, making tissue damage worse and blisters more likely.
Knowing how these processes work helps in treating fracture blisters well. By tackling the root causes and using the right treatments, doctors can help patients heal better.
Clinical Photography of Fracture Blisters
Documenting fracture blisters through clinical photography helps us understand their impact. High-quality images are key for both doctors and researchers.
Standardized Photography Techniques
For consistent and high-quality photos, follow standardized techniques. Use proper lighting, keep a set distance, and include a scale or reference object.
Key considerations for standardized photography include:
- Using a high-resolution camera
- Maintaining consistent lighting conditions
- Including a scale or reference object
- Documenting the blister from multiple angles
Documentation Best Practices
Good documentation goes beyond just taking photos. It also means how you store, label, and use the images in patient records. Best practices include:
| Documentation Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Image Labeling | Include patient ID, date, and a brief description |
| Storage | Secure, HIPAA-compliant storage solutions |
| Integration | Images should be easily accessible within patient records |
Using Images for Clinical Assessment
Clinical photos of fracture blisters are vital for assessing severity and planning treatment. They also help in patient education and communication among healthcare providers.
By using high-quality clinical photos in patient care, healthcare providers can improve diagnosis and treatment planning. This leads to better outcomes for patients with fracture blisters.
Visual Characteristics and Classification
Understanding the look of fracture blisters is key to treating them. They are mainly split into two types: clear/serous and hemorrhagic.
Clear/Serous Blisters: Appearance and Significance
Clear or serous blisters are filled with a clear fluid. They usually come from less serious injuries. Seeing clear blisters means the injury might heal faster.
Hemorrhagic Blisters: Appearance and Significance
Hemorrhagic blisters, by contrast, have blood in them. This shows a more serious injury. They can lead to infections and take longer to heal. Managing fracture blisters well means knowing these differences.
Photographic Examples and Analysis
To manage fracture blisters well, doctors need to know how to spot them. This includes looking at photos and understanding their types.
Anatomical Locations Most Prone to Fracture Blisters
Fracture blisters often appear in spots with little soft tissue and a lot of skin tension. They are a big worry in orthopedic trauma. This is because they can slow down healing and affect how well a patient does.
Ankle and Distal Tibia
The ankle and distal tibia are very likely to get fracture blisters. This is because there’s not much soft tissue there. Fractures in this area, like those at the pilon or ankle joint, often lead to blisters. Swelling and the fracture itself cause tension on the skin, leading to blisters.
Elbow Region
The elbow is also a common spot for fracture blisters, mainly with complex fractures or big soft tissue injuries. The thin soft tissue in the elbow makes it prone to blisters. Quick assessment and care are key to avoiding problems.
Other Common Sites
Fracture blisters can also happen in the foot, knee, and wrist, though less often. This depends on the injury and the patient’s health.
“Understanding the anatomical locations prone to fracture blisters is essential for effective management and prevention of complications.”
In summary, knowing where fracture blisters are most likely to occur helps healthcare workers act early. This can lower the number and effect of these issues.
Risk Factors for Developing Fracture Blisters
Fracture blisters can happen for many reasons. These include things about the patient, the injury, and how it’s treated.
Patient-Related Factors
Some things about a patient can make them more likely to get fracture blisters. Age is one, as older people’s skin is less flexible and blood flow might be worse. People with diabetes mellitus or other blood vessel problems are also at higher risk. Other factors include overall health, diet, and smoking, all of which affect how well wounds heal and skin stays strong.
Injury-Related Factors
The type and severity of the injury matter a lot. High-energy trauma and fractures that are badly broken or moved a lot are more likely to cause blisters. Where the fracture is also important. Areas like the ankle and elbow are more prone because the skin is tight and there’s little soft tissue to cushion it.
Treatment-Related Factors
How a fracture is treated can also affect the risk of blisters. Using tight casts or splints can put too much pressure on the skin, leading to blisters. The timing and type of surgery can also play a part, with early surgery being riskier if not planned well. Good wound care and dressing are key to lowering this risk.
Knowing these risk factors is key to preventing fracture blisters and managing them when they happen. By spotting high-risk patients and taking steps to prevent blisters, doctors can lower the number and severity of blisters.
Fracture Blister Symptoms and Patient Experience
Fracture blisters can cause a lot of pain and trouble for people with broken bones. It’s important to know the signs of fracture blisters to help patients get better care.
Pain and Discomfort
Fracture blisters often cause pain and discomfort. This pain can get worse when you move or put pressure on the area. The pain’s intensity can change based on the blister’s size and where it is.
Progression of Symptoms
The signs of fracture blisters can get worse over time. At first, you might see redness and swelling, then blisters form. Watching how these symptoms change is key to figuring out the right treatment.
Patient-Reported Outcomes
What patients say about their experience with fracture blisters is very helpful. They often talk about how it makes them less mobile, hurts more, and worries them about how it looks.
| Symptom | Frequency | Impact on Patient |
|---|---|---|
| Pain | High | Significant discomfort, reduced mobility |
| Swelling | Moderate | Increased pressure, possible skin breakdown |
| Blister Formation | Variable | Risk of infection, slower healing |
Diagnostic Approach to Suspected Fracture Blisters
Getting a correct diagnosis for fracture blisters is key for good care. Healthcare experts need to check everything carefully. This helps avoid problems and ensures the right treatment.
Clinical Examination Techniques
First, a detailed check-up is done to spot fracture blisters. Doctors look at the area and the patient’s overall health. Palpation and range of motion tests help find out how bad the injury is.
It’s also important to know the patient’s health history. Some conditions can make fracture blisters worse or harder to treat.
Imaging Considerations
Imaging tests are vital to confirm the diagnosis and see how serious the fracture is. X-rays check the bone injury. For soft tissue damage or complex fractures, MRI or CT scans might be needed.
Differential Diagnosis
When diagnosing fracture blisters, other conditions must be ruled out. This includes burns, infections, or skin problems. A detailed check helps make sure the right treatment is given.
Good fracture blister care and managing fracture blisters need a full diagnostic plan. This plan covers both the blisters and the fracture itself.
Impact of Fracture Blisters on Surgical Planning
Fracture blisters greatly affect how surgeons plan for orthopedic surgeries. These blisters can make surgery more complicated. This means surgeons must make careful, informed decisions.
Surgical Delay Considerations
When fracture blisters appear, surgeons might choose to delay surgery. This gives the blisters time to heal, which can lower the risk of infection. But, waiting too long can cause other problems, like longer recovery times and worse fracture damage.
Table: Factors Influencing Surgical Delay
| Factor | Description | Impact on Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Blisters Severity | Severity of fracture blisters | More severe blisters may require longer delay |
| Patient Health | Overall health of the patient | Patients with comorbidities may require adjusted surgical timing |
| Fracture Type | Type and complexity of the fracture | Complex fractures may necessitate earlier surgical intervention |
Evidence-Based Approaches
Recent studies show the need for evidence-based methods in treating fracture blisters. These include proper wound care and watching for complications. Advanced wound dressings and topical treatments can help prevent infections and aid in healing.
Decision-Making Algorithm
A decision-making algorithm is helpful for surgeons dealing with fracture blisters. It considers the blisters’ severity, the fracture type, and the patient’s health. This way, surgeons can make better decisions about when and how to operate.
In conclusion, fracture blisters have a big impact on surgical planning. They require careful thought and the use of proven methods. By understanding these issues and using evidence-based approaches, surgeons can improve surgical results.
Fracture Blister Treatment: Conservative Management
Effective treatment of fracture blisters needs a deep understanding of how to care for blisters. This method is key for healing wounds, avoiding complications, and better patient results.
Blister Care Principles
Good blister care is the base of conservative management. It means keeping the area clean, protecting it from more harm, and keeping it moist for healing. Protective dressings are very important in this process.
Topical Treatments and Medications
Topical treatments and medicines help manage symptoms and aid healing. Antibiotic ointments prevent infection, and pain medicines reduce discomfort from fracture blisters.
Dressing Selection and Application Techniques
Choosing and applying dressings is a big part of caring for fracture blisters. Different dressings, like hydrocolloid and foam, are used based on the blister and patient’s needs.
Specialized Dressings
Special dressings, like those with antimicrobial properties, offer extra benefits for fracture blisters. They help lower infection risk and support healing.
Frequency of Dressing Changes
How often to change dressings depends on the dressing and patient’s situation. Dressings should be changed when they get dirty or damaged, or as a doctor advises.
In summary, treating fracture blisters conservatively involves many steps. These include proper care, topical treatments, and choosing the right dressings. By knowing and using these steps, healthcare teams can improve patient care and results.
Surgical Considerations in the Presence of Fracture Blisters
When fracture blisters are present, planning surgery carefully is key. These blisters can change how surgery is done, to keep risks low.
Incision Planning and Alternatives
Planning where to make an incision is very important with fracture blisters. Alternative incision sites might be needed to skip blister areas. Surgeons must think about the pros and cons of each option.
- Careful assessment of blister location and size
- Consideration of alternative surgical approaches
- Use of minimally invasive techniques when possible
Soft Tissue Handling Techniques
It’s important to handle soft tissues gently to avoid more damage and help healing. Using minimal dissection and careful retraction can reduce tissue harm.
Postoperative Wound Care Protocols
Good care after surgery is key to avoid problems and help healing. This includes meticulous wound care and watching for signs of infection or other issues.
- Regular dressing changes
- Surveillance for infection
- Patient education on wound care
By taking a thoughtful and detailed approach to surgery, healthcare providers can improve outcomes for patients with fracture blisters. This helps lower the chance of fracture blister complications.
Preventing Fracture Blisters in High-Risk Patients
To prevent fracture blisters in high-risk patients, we need a mix of strategies. This approach aims to lower the risk of these issues.
Early Intervention Strategies
Acting fast is key in stopping fracture blisters. We must quickly check and treat the injury. This includes reducing and stabilizing the fracture. Early action can lessen tissue tension and cut down blister risk.
Optimal Splinting and Immobilization
Using the right splinting and immobilization methods is vital. Well-padded splints and careful immobilization can ease skin pressure. This helps prevent blisters from forming.
Pharmacological Approaches
Medicine can also help prevent fracture blisters. Anti-inflammatory medications can reduce swelling and inflammation. These are factors that increase blister risk.
Patient Education
Teaching patients about fracture blister care is important. They should know how to watch for blisters and when to see a doctor. This knowledge is key to prevention.
By using these methods, healthcare teams can lower fracture blister rates in at-risk patients. This improves outcomes and lessens complications.
Complications Associated with Fracture Blisters
It’s important to know about the problems fracture blisters can cause. These issues can affect how well a patient heals and their overall health.
Infection Risk and Management
Fracture blisters can make infections more likely, which is a big concern. Infection control measures are key to stopping infections from spreading. A study in the Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma found that blisters increase the chance of infections after surgery.
“The presence of fracture blisters significantly increases the risk of surgical site infections.”
To manage this risk, it’s vital to take good care of the wound and watch for any signs of infection.
Delayed Wound Healing
Fracture blisters can also slow down healing. They make the healing process more complicated, needing extra care and strategies.
| Factor | Impact on Healing |
|---|---|
| Fracture Blisters | Delays healing process |
| Infection | Significantly delays healing |
| Wound Care | Improper care can delay healing |
Long-Term Skin Changes
Fracture blisters can also cause lasting changes to the skin. These changes include scarring and changes in skin color.
Scarring
Scarring is a common issue from fracture blisters. The extent of scarring depends on the size and depth of the blisters.
Pigmentation Changes
Changes in skin color can also happen. These can be permanent if not treated right.
In summary, fracture blisters can lead to several problems. These include infection risk, slower healing, and lasting skin changes. Knowing about these issues is key to giving good care.
Fracture Blister Healing Time and Recovery Process
Fracture blisters are common in orthopedic trauma. They have a healing timeline that doctors need to know. The healing process goes through several stages, from blister formation to their disappearance.
Expected Timeline for Resolution
Fracture blisters usually heal in 1-2 weeks. The first step is when blisters form. They can be clear or filled with blood. Then, the blisters dry out and the skin heals over.
Factors Affecting Healing Speed
Many things can affect how fast blisters heal. The severity of the fracture and any infections are big factors. Smoking and poor blood flow can also slow healing.
Monitoring Progress
It’s important to keep an eye on how blisters are healing. Doctors check their size, color, and look. They watch for signs of infection or other problems.
When to Seek Additional Medical Attention
If you have more pain, signs of infection, or blisters not healing, see a doctor. Early help can stop bigger problems later.
| Healing Stage | Timeline | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Formation | 0-3 days | Blisters form, can be clear or hemorrhagic |
| Drying Out | 3-7 days | Blisters start to dry out, skin begins to re-epithelialize |
| Re-epithelialization | 7-14 days | Skin fully re-epithelializes, blisters resolve |
Conclusion: Clinical Importance and Future Research Directions
Fracture blisters are a big problem in orthopedic trauma. They affect how well patients do and what treatments they need. It’s key for doctors to know about them.
Fracture blisters make surgery and healing harder. But, research is moving forward. It’s looking into better ways to treat and prevent them.
Future studies might look at new wound care products. They could also study how fracture blisters affect patients long-term. This could help make care better for everyone.