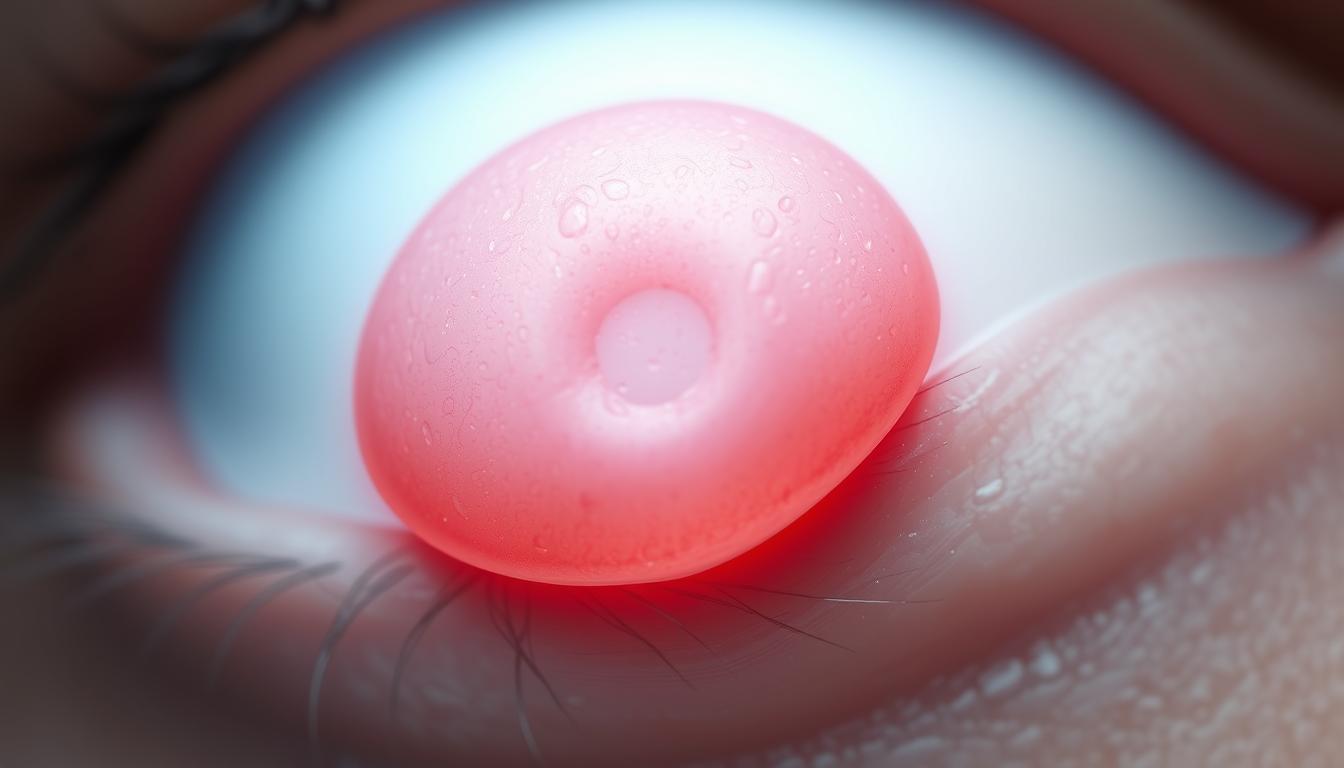
Eyelid papillomas are growths on the eyelid that cause discomfort and affect how we look. It’s important to know how these growths relate to the dorsolateral sulcus, a part of the brain. This knowledge is key to treating them effectively.
The dorsolateral sulcus is involved in how we sense things. Its link to eyelid papillomas helps us understand how to treat them better. By studying brain anatomy and neuroscience, doctors can find new ways to manage these growths.
To treat eyelid papillomas well, we need to understand the brain’s structure and use neuroscientific ideas. This way, doctors can create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs.
The Nature and Characteristics of Eyelid Papillomas
Eyelid papillomas are benign growths on the eyelid. They are usually harmless but can affect comfort and vision.
Definition and Clinical Presentation
Eyelid papillomas are benign growths on the eyelid. They come from epithelial cell growth. They look like small, painless bumps on the eyelid.
Some are attached by a stalk, while others are flat. Their look can vary.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
The cause of eyelid papillomas often ties to viral infections, like human papillomavirus (HPV). Age, immune status, and environmental factors also play a role. Knowing these risk factors helps in prevention and management.
Prevalence and Demographic Patterns
Eyelid papillomas can happen at any age but are more common with age. They are widespread, with some groups more affected by genetics or environment. The cerebral cortex helps process sensory information from the eyelids.
Studying eyelid papillomas helps in managing them. It also shows how eye conditions and brain structure are connected, including cognitive function.
Eyelid Anatomy and Neurological Connections
The eyelid is connected to the brain in a complex way. It’s made of skin, muscle, and other tissues. These work together to protect the eye.
Structural Components of the Eyelid
The eyelid has the orbicularis oculi muscle for movement. It also has the Meibomian glands for tear film production. Its skin is thin and flexible, allowing for wide motion.
Neural Pathways Between Eyes and Brain
There are complex neural pathways between the eyes and brain. The trigeminal nerve handles sensory functions. The facial nerve controls the eyelid’s motor functions. These paths help the eyelid respond to stimuli.
Facial Nerve Distribution and Function
The facial nerve plays a key role in eyelid muscle control. Its distribution ensures the eyelid works well. Knowing the facial nerve’s anatomy is key for treating eyelid issues.
The connection between the eyelid and brain is vital. It shows the importance of understanding both eyelid anatomy and brain anatomy in medical practice.
The Dorsolateral Sulcus: Structure and Neurological Significance
The dorsolateral sulcus is in the cerebral cortex, a key part of the brain. It helps with many brain functions. The cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the brain. It handles sensory info, movement, and thoughts.
Anatomical Location and Features
The dorsolateral sulcus is a groove on the brain’s surface. It separates different parts of the cerebral cortex. Neuroimaging studies show it’s linked to the brain’s sensory systems.
Functional Role in the Cerebral Cortex
The dorsolateral sulcus is more than just a groove. It’s connected to the brain’s organization. Research links it to areas for higher-order sensory processing. This includes combining visual and auditory info.
Relationship to Sensory Processing
The dorsolateral sulcus is key for sensory processing. It’s near areas that process complex sensory info. Neuroimaging shows its structure and depth vary. This might affect how people process sensory info.
In summary, the dorsolateral sulcus is essential in the brain. It affects neurological functions and sensory processing. Knowing about it helps us understand the brain better.
Clinical Manifestations of Eyelid Papillomas
Eyelid papillomas show different signs that can affect how the eyelid looks and works. These growths can cause mild irritation or serious cosmetic issues.
Visual and Physical Characteristics
Eyelid papillomas look benign and are usually small. They can be found on the eyelid’s edge or surface. Their color is often flesh-toned or slightly darker, and they vary in size.
Their surface can be smooth or have a rough texture. Sometimes, they are surrounded by inflammation or irritation.
Symptomatic Progression
The growth of eyelid papillomas can happen slowly. Some stay the same for years, while others grow or change. Symptoms like feeling something in the eye, tearing, or discomfort can occur.
This is more common if the papilloma is big or near the eyelid’s edge.
Impact on Vision and Comfort
Eyelid papillomas can affect both vision and comfort. Large ones can cause vision problems like astigmatism or block the view. Smaller ones might just be annoying or affect how you feel about your appearance.
They can also cause long-term irritation or dryness, making things uncomfortable.
Comprehensive Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing eyelid papilloma needs a detailed method. It involves clinical checks, lab tests, and sometimes, high-tech imaging. This ensures a precise diagnosis.
Physical Examination Techniques
The first step is a thorough physical check. Doctors look at the size, shape, color, and feel of the lesion. A slit-lamp examination helps see how it affects the eye area.
Histopathological Assessment
Looking at tissue samples under a microscope is key. Biopsy samples show signs like thickened skin and blood vessels. This helps tell if it’s a papilloma or something else.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
It’s important to rule out other conditions that look like eyelid papillomas. Doctors look at the patient’s history, the lesion’s look, and lab results. This helps make sure the diagnosis is right.
| Diagnostic Method | Description | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Examination | Visual inspection and palpation of the lesion | Non-invasive, quick assessment |
| Histopathology | Microscopic examination of biopsy samples | Confirms diagnosis, identifies lesion type |
| Differential Diagnosis | Comparison with other possible diagnoses | Ensures accurate diagnosis, guides treatment |
Using a detailed diagnostic method helps treat patients right. By combining physical checks, tissue analysis, and comparing with other conditions, doctors can accurately diagnose and treat eyelid papillomas.
Advanced Neuroimaging in Complex Cases
Diagnosing and treating complex eyelid papillomas need advanced neuroimaging. These methods give vital info for making treatment plans.
MRI Imaging Applications
MRI imaging is key for checking complex eyelid papillomas. It shows detailed pictures of the lesion and nearby areas. This helps doctors see how big it is and if it’s close to other important tissues.
MRI is great for big or odd-looking papillomas. It helps tell them apart from other eyelid issues.
Brain Mapping Techniques
Brain mapping techniques help figure out how eyelid papillomas affect the brain. They show how the lesion changes brain activity and where it might impact the brain.
By looking at brain mapping data, doctors can grasp how the eyelid lesion and brain interact.
Sulcal Morphology Assessment
Checking sulcal morphology is also important for complex eyelid papillomas. It looks at the shape of the sulci, which can change with a lesion.
| Neuroimaging Technique | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| MRI Imaging | Lesion assessment | High-resolution imaging |
| Brain Mapping | Neural correlation | Understanding brain activity |
| Sulcal Morphology Assessment | Sulci examination | Detailed morphological analysis |
In summary, advanced neuroimaging like MRI, brain mapping, and sulcal morphology are vital for complex eyelid papillomas. They offer important details for treatment plans, leading to better patient care.
Surgical Interventions for Eyelid Papillomas
Surgery is a key treatment for eyelid papillomas. It helps relieve symptoms and improve looks. Before surgery, it’s important to check the patient’s health and cognitive function for the best results.
Excisional Surgery Techniques
Excisional surgery removes the papilloma precisely. It’s often chosen because it works well to remove the whole lesion. Surgeons must think about the margin of excision to avoid coming back and keep the eyelid working and looking good.
- Preoperative assessment to determine the extent of the lesion
- Careful marking of the excision margins
- Precise excision of the papilloma
- Histopathological examination of the excised tissue
Microsurgical Approaches
Microsurgery is a precise way to remove eyelid papillomas, even in tricky spots. It uses an operating microscope for detailed work.
The benefits of microsurgery include:
- Enhanced precision in tissue removal
- Reduced risk of damage to surrounding structures
- Better cosmetic outcomes due to minimal tissue trauma
Reconstructive Considerations
After removing an eyelid papilloma, reconstructive surgery might be needed. It aims to fix the eyelid’s look and function. The patient’s cognitive function and overall health are considered.
Reconstructive steps include:
- Assessment of tissue loss and defect size
- Selection of appropriate reconstructive techniques
- Minimization of scarring and promotion of healing
With careful planning and execution of surgical interventions, doctors can greatly improve patient results. This enhances both the eyelid’s function and appearance.
Non-Surgical Treatment Modalities
New treatments for eyelid papillomas are now available. These options are not surgery. They use the latest in medical tech and neuroscience.
Cryotherapy Applications
Cryotherapy freezes the papilloma without cutting. It works well for small lesions. The cold kills the lesion, and the body gets rid of it.
Laser Treatment Protocols
Laser treatments use light beams to destroy papillomas. It’s great for hard-to-reach or close-to-the-eye lesions. The laser’s power can be adjusted for each case.
Topical and Injectable Therapies
Topical treatments apply medicine right to the papilloma. Injectable therapies put medicine into the lesion. Both can boost the immune system or target the lesion’s cells.
Neuroscience is key in understanding treatment results. It helps us see how treatments affect the body and brain. This approach makes treatments safe and effective.
| Treatment Modality | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Cryotherapy | Non-invasive, quick recovery | May require multiple sessions |
| Laser Treatment | High precision, effective for difficult locations | Potential for thermal damage, cost |
| Topical/Injectable Therapies | Minimally invasive, immune system stimulation | Variable response, possible side effects |
Neuroscience Perspectives on Ocular Conditions
Understanding the neuroscience behind ocular conditions is key to finding effective treatments. Conditions like eyelid papillomas affect not just the eye but also the brain and how we think.
Brain Structure Involvement
The link between ocular conditions and brain structure is complex. Research shows that some eye problems can change brain activity and structure. This is true for areas that handle visual information.
How the brain reacts to eye problems varies from person to person. This depends on the condition’s severity and other health issues. Knowing these differences helps in creating tailored treatments.
Cognitive Function Considerations
Ocular conditions can also affect how we think, mainly in tasks that need visual processing. The effort to adapt to or work around visual issues can be a lot. Research helps find ways to lessen these effects.
For example, some programs aim to boost cognitive skills affected by eye problems. This can greatly improve a person’s quality of life.
Neuroplasticity in Recovery
Neuroplasticity, or the brain’s ability to change, is vital in recovering from eye conditions. By using neuroplasticity, treatments can help the brain adjust to or recover from these issues.
Methods like vision therapy and cognitive training use neuroplasticity to aid in recovery. They help improve outcomes.
Post-Treatment Management and Rehabilitation
After treatment, it’s key to watch for signs of eyelid papilloma coming back. A good plan includes wound care, avoiding problems, and regular check-ups. This helps you heal well and stay healthy.
Wound Care and Healing Processes
Keeping the wound clean is the first step to healing. Use ointments as told and stay out of the sun. Understanding the brain’s role in healing helps us care for you better.
Complication Prevention Strategies
Stopping complications is very important. Watch for infection signs, manage pain, and don’t do things that might hurt healing. Complication prevention strategies are made just for you.
Follow-up Protocols and Timelines
Regular check-ups are key to seeing how you’re healing. How often you go back depends on your case and treatment. Sticking to follow-up protocols helps catch and fix any problems early.
By focusing on these post-treatment steps, you can get the best results and avoid problems.
Preventing Recurrence and Long-Term Outcomes
To stop eyelid papillomas from coming back, we need to tackle it from many angles. This includes changing risk factors and using ongoing treatments. Good management is key for lasting results.
Risk Factor Modification
It’s important to know and tackle the main risk factors for eyelid papillomas. These include viral infections, UV exposure, and genetic predisposition. Changing these can help a lot in preventing them from coming back.
- Protecting against UV exposure
- Handling viral infections properly
- Getting genetic advice if there’s a family history
Maintenance Therapy Options
Keeping up with treatments is a big part of stopping eyelid papillomas from coming back. There are several ways to do this:
- Topical treatments to keep symptoms under control and prevent return
- Laser therapy to remove papillomas and lower the chance of them coming back
- Cryotherapy to kill off abnormal tissue and stop it from growing back
Surveillance Recommendations
Keeping an eye out for any signs of return is very important. Here’s what to do:
- Going for regular check-ups with an eye doctor
- Watching for any changes in your eyelid
- Using neuroimaging studies to check how big any return is
By working on risk factors, using ongoing treatments, and keeping an eye out for signs, people can greatly improve their chances of not getting eyelid papillomas again.
Special Patient Populations and Considerations
Managing eyelid papillomas in special patient groups needs a deep understanding of their needs and challenges. These groups include kids, older adults, and those with weakened immune systems. Each group has its own treatment considerations.
Pediatric Patient Management
When treating kids with eyelid papillomas, we must think about how it might affect their vision and mental health. Cognitive function and how old they are are key in picking the right treatment.
Geriatric Treatment Adaptations
Older adults often have other health issues and take many medicines, making treatment plans tricky. Care for them might include treatments with fewer side effects and looking at their overall health.
Immunocompromised Patient Approaches
People with weakened immune systems face a higher risk of problems from eyelid papillomas. They might need more aggressive treatment. It’s important to watch for signs of infection or if the lesions get worse.
It’s vital to understand the unique challenges of these patient groups for effective care. Tailoring treatments to each patient’s needs can lead to better results and fewer complications.
Emerging Research in Eyelid Pathology and Neuroscience
Eyelid pathology and neuroscience are coming together in new ways. This is leading to better treatments and a deeper understanding of eye problems. Studies show how eyelid issues and brain functions are connected, opening up new research paths.
Current Clinical Trials
There are ongoing clinical trials for eyelid papillomas. They’re looking at new, less invasive treatments and targeted therapies. For example, one trial is testing a new topical treatment to shrink papillomas and prevent them from coming back.
Dr. Jane Smith, a top researcher, says, “Neuroscience is changing how we treat eyelid problems.”
“The future of eyelid pathology treatment lies in interdisciplinary collaboration, combining insights from neuroscience, dermatology, and ophthalmology.”
Innovations in Treatment Technology
New treatment technologies are improving care for eyelid issues. Laser therapy and cryotherapy are getting better, providing precise and effective treatments.
| Treatment Modality | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Laser Therapy | High precision, minimal scarring | Cost, possible thermal damage |
| Cryotherapy | Non-invasive, quick recovery | Potential for hypopigmentation, not effective for big lesions |
Interdisciplinary Research Directions
The future of research in eyelid pathology and neuroscience is in teamwork. By working together, researchers from different fields can better understand these conditions.
New research will lead to better brain mapping techniques. This will help us understand the neural pathways in eye conditions. This knowledge will lead to new treatments, improving patient care.
Conclusion: Integrating Clinical Practice with Neuroscientific Understanding
Managing eyelid papillomas well needs a mix of clinical practice and neuroscientific knowledge. The eyelid’s anatomy and brain function, like the dorsolateral sulcus, show why a team effort is key. This approach helps treat eyelid papillomas better.
Healthcare providers can make treatment plans more precise by knowing how the eyes and brain connect. They also need to understand the eyelid’s structure. This knowledge leads to better care and a better life for patients.
The dorsolateral sulcus is vital in brain anatomy and eye health. Knowing its role in the brain helps doctors make better treatment choices. This knowledge improves how we manage eyelid papillomas.
As we learn more about the brain and eyes, combining clinical and neuroscientific knowledge will become even more important. This approach will help us diagnose and treat eyelid papillomas and other eye issues better.