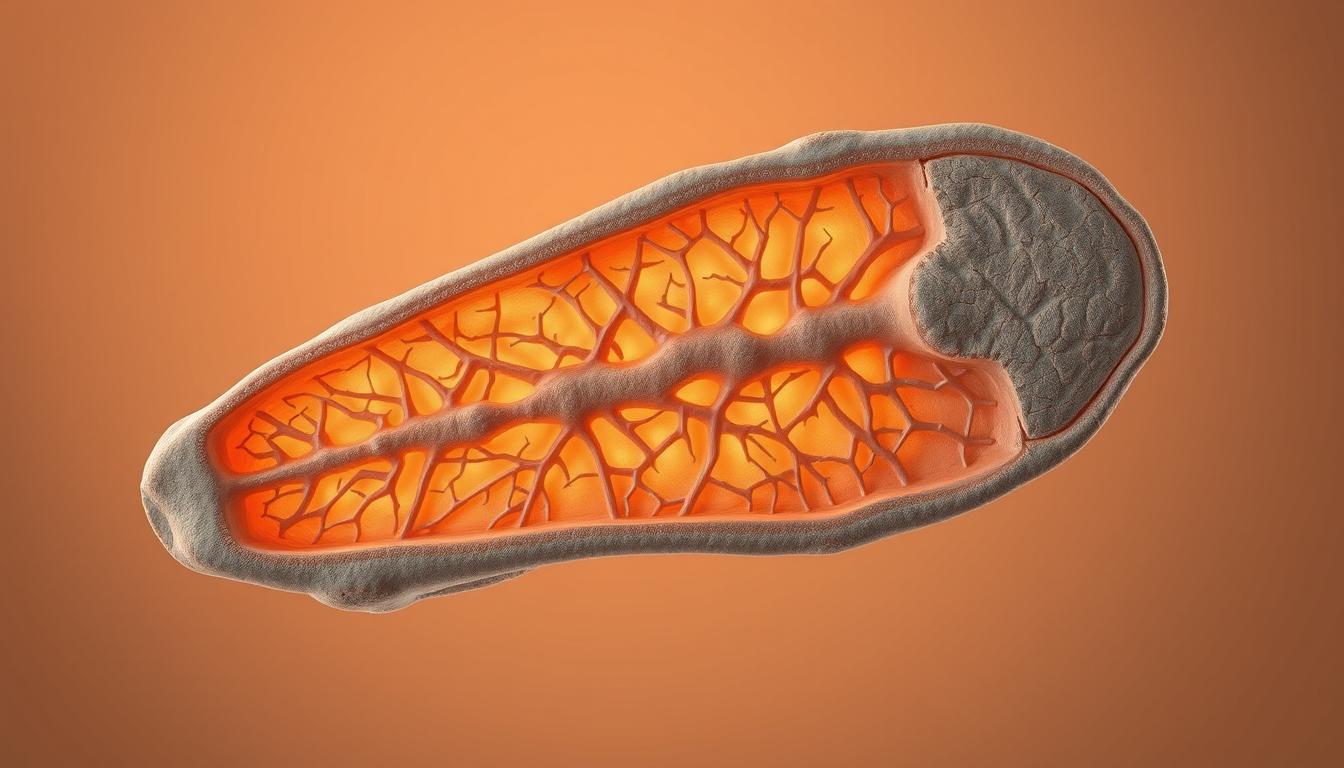
Volkmann’s canals are key in bone anatomy and bone physiology. They help blood vessels reach the bones from the periosteum. This exchange is vital for nutrients and waste.
Volkmann’s canals are important for bone health. They allow blood vessels to bring nutrients and oxygen to the bone tissue.
Knowing how Volkmann’s canals work helps us understand bone physiology. This includes how bones are remodeled and repaired.
What Are Volkmann’s Canals?
Named after German physiologist Alfred Volkmann, these canals are key to bone structure. Volkmann’s canals, or perforating holes, are vital for bone health and function.
Definition and Basic Anatomy
Volkmann’s canals are perforating channels that link Haversian canals. They help exchange nutrients, waste, and blood in bone tissue. This is essential for bone cells to get what they need for proper function.
Historical Background and Discovery
German physiologist Alfred Wilhelm Volkmann discovered Volkmann’s canals. His work added to our understanding of anatomy’s history.
Alfred Wilhelm Volkmann’s Contributions
Alfred Wilhelm Volkmann’s research on bone vascular systems shed light on Volkmann’s canals. His findings showed their role in bone physiology. This opened doors for more studies on bone anatomy and its functions.
| Key Features | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Connect Haversian canals, facilitating nutrient and waste exchange |
| Structure | Perforating channels within the bone tissue |
| Importance | Crucial for bone health and function |
Anatomical Structure of Volkmann’s Canals
Understanding Volkmann’s canals is key to knowing how bones work. These canals are vital for bringing nutrients and oxygen to bone cells. They are a big part of the bone’s vascular system.
Microscopic Appearance
When we look at Volkmann’s canals under a microscope, we see channels in the bone. These channels have blood vessels and nerves. They are important for keeping bone cells healthy.
Distribution Throughout Bone Tissue
Volkmann’s canals spread out in bone tissue, linking up with other channels. They don’t just appear randomly. Their pattern is key for delivering nutrients well.
Orientation and Patterns
The way Volkmann’s canals are arranged is unique. They often run at right angles to Haversian canals. This setup helps the bone stay strong.
To wrap it up, Volkmann’s canals are very important for bone health. Their structure, including how they look under a microscope and their layout, helps bones get what they need. This supports the bone’s overall health.
The Primary Function of Volkmann’s Canals in Bone Physiology
Volkmann’s canals are key in transporting blood and nutrients to bone cells. They help keep bone tissue healthy and strong.
Blood Supply Transportation
Volkmann’s canals are vital for blood supply in bones. They link Haversian canals, making sure bone cells get oxygen and nutrients. This network is vital for the survival of osteocytes, the cells embedded within the bone matrix.
Nutrient Distribution
They also play a big role in delivering nutrients to bone cells. This supports bone growth and upkeep.
Oxygen and Mineral Delivery
Delivering oxygen and minerals is key. Volkmann’s canals make sure these vital resources reach bone cells. A leading researcher says, “The network of Volkmann’s canals is essential for bone metabolism balance.”
“The network of Volkmann’s canals is essential for bone metabolism balance.”
| Function | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Supply | Transportation of blood throughout the bone | Essential for osteocyte survival |
| Nutrient Distribution | Delivery of nutrients to bone cells | Supports bone growth and maintenance |
| Oxygen and Mineral Delivery | Transportation of oxygen and minerals | Critical for bone cell metabolism |
In summary, Volkmann’s canals are vital for bone health. They help transport blood and nutrients. Their role in delivering oxygen and minerals is key to maintaining bone health.
Relationship Between Volkmann’s Canals and Haversian Systems
The connection between Volkmann’s canals and Haversian systems is key to bone health. Volkmann’s canals link Haversian canals to the periosteum. This allows for the exchange of nutrients and waste in bone tissue.
Structural Connections
Volkmann’s canals and Haversian systems form a complex network. Volkmann’s canals run across the bone, meeting Haversian canals at right angles. This creates a vast vascular network.
This network is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to bone cells. It supports bone health by ensuring these cells get what they need.
Functional Integration
The integration of Volkmann’s canals with Haversian systems is vital for bone upkeep. Volkmann’s canals help move nutrients and waste. Haversian systems, with their concentric lamellar structure, house blood vessels and nerves.
Complementary Roles in Bone Maintenance
Volkmann’s canals and Haversian systems play important roles in bone health. Here’s how:
- Nutrient and waste exchange by Volkmann’s canals.
- Osteocyte nourishment through the vascular network.
- Support for bone remodeling processes.
In summary, the bond between Volkmann’s canals and Haversian systems is critical. It ensures bone health by efficiently supplying nutrients and removing waste.
Volkmann’s Canals in Different Types of Bones
Volkmann’s canals have different roles in long, flat, and irregular bones. Knowing how they work in each is key to understanding bone health and problems.
Long Bones
In long bones, like the femur and humerus, Volkmann’s canals are very important. They help connect the bone’s surface to its inside. This lets nutrients and waste move around efficiently. Long bones need these canals to stay strong and work right.
Flat Bones
Flat bones, like the sternum and skull bones, also have Volkmann’s canals. But they’re arranged differently than in long bones. These canals help spread blood vessels and nutrients. They’re vital for keeping flat bones healthy.
Irregular Bones
Irregular bones, like vertebrae and the pelvis, have unique Volkmann’s canals. These canals help meet the special needs of these bones. They’re important for the overall health of the skeleton.
Development of Volkmann’s Canals During Bone Growth
Volkmann’s canals are key in bone growth, starting from when we’re in the womb. They are important for the bone’s structure and function.
Embryonic Formation
In the womb, Volkmann’s canals form alongside the Haversian systems. These canals act as paths for nutrients and waste in the bone tissue.
Changes Throughout Lifespan
Volkmann’s canals change a lot as we grow older. As bones grow and change, so do these canals. They adapt to the bone’s needs.
Age-Related Modifications
With age, Volkmann’s canals can get denser or wider. This affects bone health. Here’s a table showing these changes.
| Age Group | Changes in Volkmann’s Canals |
|---|---|
| Young | High density, smaller diameter |
| Adult | Moderate density, moderate diameter |
| Old | Lower density, larger diameter |
Knowing about these changes helps us understand how Volkmann’s canals keep bones healthy all our lives.
Cellular Components Associated with Volkmann’s Canals
Volkmann’s canals are not just simple channels. They are complex structures that house various cellular components. These cells are essential for bone function.
Osteocytes
Osteocytes are the most abundant cell type in bone tissue. They are found within the lacunae surrounding Volkmann’s canals. These cells play a vital role in bone remodeling and mineral ion homeostasis.
Osteocytes communicate with each other and with cells on the bone surface through a network of canaliculi. This allows for the coordination of bone resorption and formation.
Blood Vessel Cells
Blood vessel cells, including endothelial cells and pericytes, are found within Volkmann’s canals. These cells are essential for the vascular supply that nourishes bone tissue. The endothelial cells line the blood vessels, while pericytes surround the endothelial cells, providing structural support.
Supporting Cells
Supporting cells, such as osteoblasts and osteoclasts, are also associated with Volkmann’s canals. Osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation, while osteoclasts are involved in bone resorption. The balance between these two cell types is critical for maintaining bone health.
| Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Osteocytes | Maintain bone health, regulate mineral ion homeostasis |
| Blood Vessel Cells | Provide vascular supply, support bone tissue |
| Osteoblasts | Form bone matrix, promote bone mineralization |
| Osteoclasts | Resorb bone tissue, regulate bone remodeling |
A leading researcher notes, “The relationship between Volkmann’s canals and the surrounding cellular components is key to understanding bone physiology and pathology.” This shows the importance of studying these structures in detail.
Volkmann’s Canals and Bone Remodeling Processes
Volkmann’s canals play a key role in bone remodeling. They help control the work of osteoclasts and osteoblasts through different signals. These canals are vital for bone health, allowing nutrients, waste, and signals to move between bone cells and blood.
Osteoclast Activity and Volkmann’s Canals
Osteoclasts are big cells that break down bone. Volkmann’s canals help osteoclasts reach different parts of the bone. This makes it easier for them to do their job.
The canals also have blood vessels. These vessels give osteoclasts the oxygen and nutrients they need to work.
Many factors control osteoclasts in Volkmann’s canals. For example, the RANK/RANKL pathway is key for their growth and action. The canals help move these important molecules, affecting osteoclast work.
Contribution to Osteoblast Function
Osteoblasts are cells that build bone. Volkmann’s canals help osteoblasts by spreading out bone-building factors and cells. This lets osteoblasts reach where bone needs to grow.
Signaling Pathways
Signaling pathways are important for both osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Volkmann’s canals carry molecules like BMPs and Wnts, which are key for bone growth and repair. These pathways keep bone resorption and formation in balance, keeping bones healthy.
The connection between Volkmann’s canals, osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and signals shows how complex bone remodeling is. Knowing this helps us understand bone health and disease better.
- Volkmann’s canals facilitate osteoclast and osteoblast activity.
- Signaling pathways within these canals regulate bone remodeling.
- The canals are critical for nutrient and waste distribution.
Physiological Processes Facilitated by Volkmann’s Canals
Volkmann’s canals are more than just structures in our bones. They help keep our bones healthy and strong. These canals connect the Haversian systems, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, waste, and signals.
Mineral Homeostasis
Volkmann’s canals help manage minerals like calcium and phosphorus. They move these minerals to and from bone cells. This is key for keeping bones strong and storing minerals.
Waste Removal
These canals also help get rid of waste from bones. It’s important to remove waste to protect bone cells and keep bone remodeling going smoothly.
Hormone Transport
Volkmann’s canals also carry hormones that control bone health. Hormones like parathyroid hormone and calcitonin are vital for bone growth and breakdown. They make sure these processes work right.
A study on bone health shows how important Volkmann’s canals are. They help keep bones healthy by moving nutrients and waste.
“The canals allow for the efficient distribution of minerals and hormones, underscoring their importance in bone physiology.”
Here’s a quick look at what Volkmann’s canals do:
| Process | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Mineral Homeostasis | Transport of minerals like calcium and phosphorus | Maintains bone integrity and mineral balance |
| Waste Removal | Removal of metabolic waste products | Prevents accumulation of harmful byproducts |
| Hormone Transport | Delivery of hormones regulating bone metabolism | Regulates bone resorption and formation |
Clinical Significance of Volkmann’s Canals
Volkmann’s canals are key for bone graft success in orthopedic surgery. They help with blood flow and bone health.
Importance in Orthopedic Surgery
In orthopedic surgery, knowing about Volkmann’s canals is vital. They help with blood flow to bones, which is important for healing. Effective vascularization is key for successful surgeries.
Relevance to Bone Grafting Procedures
Bone grafting needs Volkmann’s canals to work well. They help the grafted bone get the blood it needs. Proper vascularization is essential for the graft to work with the host bone.
Vascularization Considerations
Vascularization is very important for bone graft success. Volkmann’s canals help by providing blood vessel paths. Surgeons must look at these canals when planning bone graft surgeries.
Understanding Volkmann’s canals is important for better bone health and surgery. This knowledge helps improve patient care and surgery results.
Pathological Conditions Affecting Volkmann’s Canals
Pathological conditions can harm Volkmann’s canals, which are key for bone health. They help transport blood and nutrients. But, diseases can damage them.
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis weakens bones, making them more likely to break. It damages Volkmann’s canals by lowering bone density. This hurts bone health.
Impact on Bone Viability: Osteoporosis can reduce blood and nutrient flow. This might lower bone viability.
Osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis happens when bones lose blood. Volkmann’s canals are vital for blood supply. Without it, bone tissue can die.
“Osteonecrosis is a serious condition that can lead to the collapse of bone structure, significantly impacting the quality of life.”
Bone Infections
Bone infections, like osteomyelitis, harm Volkmann’s canals. They spread through the blood and damage bone tissue.
Impact on Bone Viability
Bone infections can severely damage Volkmann’s canals. This can lower bone viability. Untreated infections can cause lasting health problems.
| Pathological Condition | Effect on Volkmann’s Canals | Impact on Bone Viability |
|---|---|---|
| Osteoporosis | Reduces bone density and alters microarchitecture | Decreases bone viability due to impaired nutrient and blood supply |
| Osteonecrosis | Compromises blood supply through Volkmann’s canals | Leads to death of bone tissue |
| Bone Infections | Damages Volkmann’s canals and disrupts function | Reduces bone viability, potentially causing long-term damage |
Diagnostic Imaging and Assessment of Volkmann’s Canals
Diagnostic imaging is key in checking Volkmann’s canals. It helps us see how they work and what they look like. Knowing about these canals is important for bone health and finding bone problems.
Microscopy Techniques
Microscopy is a big help in studying Volkmann’s canals. Light microscopy and electron microscopy let us see the canals up close. They give us details about the canals and the bone around them.
Advanced Imaging Methods
New imaging methods have changed how we study Volkmann’s canals. Micro-CT and high-resolution MRI let us see the canals in 3D. This gives us important info about their shape and how they work.
Micro-CT Applications
Micro-CT is great for looking at Volkmann’s canals because it shows them clearly in 3D. It helps us measure the canals and where they are in the bone.
Thanks to micro-CT, we know more about Volkmann’s canals. It helps us link their structure to bone function and diseases.
Volkmann’s Canals in Bone Healing and Repair
Volkmann’s canals are key for bone fracture healing. They help move nutrients and waste. This is vital for bone repair.
Response to Fractures
When a bone breaks, the body sends more blood to fix it. Volkmann’s canals are important here. They help bring the blood needed for healing.
“The rapid re-establishment of blood supply is critical for the initiation of the bone healing process,” say orthopedic surgery experts.
“The presence of Volkmann’s canals ensures that the bone tissue receives the necessary nutrients and oxygen for repair.”
Role in Bone Regeneration
Volkmann’s canals also help in bone regeneration. They let cells like osteoblasts and osteoclasts move. This boosts bone repair.
Understanding Volkmann’s canals’ role in healing is important. It could lead to better treatments for bone issues. For example, treatments that help these canals could heal bones faster.
By studying Volkmann’s canals, we can find better ways to keep bones healthy.
Comparative Anatomy: Volkmann’s Canals Across Species
Volkmann’s canals are found in many mammals, not just humans. Each species has its own version, shaped by its needs. This shows how these canals have evolved to help different animals.
Mammalian Variations
In big animals like elephants and whales, Volkmann’s canals are bigger and more detailed. They help these huge creatures get nutrients and oxygen to their bones. On the other hand, smaller animals like mice have smaller canals. Yet, they are just as important for their bone health.
As a leading anatomist noted, “The variation in Volkmann’s canals across species shows how bones adapt to different needs.”
Evolutionary Significance
Volkmann’s canals are key to understanding how mammals evolved. They help explain why bones vary in size and function. From the tiny bones of bats to the strong bones of big cats, these canals play a vital role.
Evolutionary biologists suggest that keeping these canals is important for bone health. It shows how strong the need is for efficient bone vascularization.
In summary, studying Volkmann’s canals across species helps us understand anatomy and evolution. It shows how mammals have adapted their bones over time.
Conclusion: The Essential Role of Volkmann’s Canals in Skeletal Health
Volkmann’s canals are key to keeping bones healthy. They help move blood and nutrients to bone tissue. This is important for bone cells to work right.
Bone cells like osteocytes, osteoblasts, and osteoclasts need this to keep bones strong. They help bones grow and stay healthy.
The network of Volkmann’s canals and Haversian systems shows how complex bones are. Knowing about Volkmann’s canals helps us understand bone health and diseases.
In short, Volkmann’s canals are vital for bone health. Studying them could lead to new ways to prevent and treat bone problems.