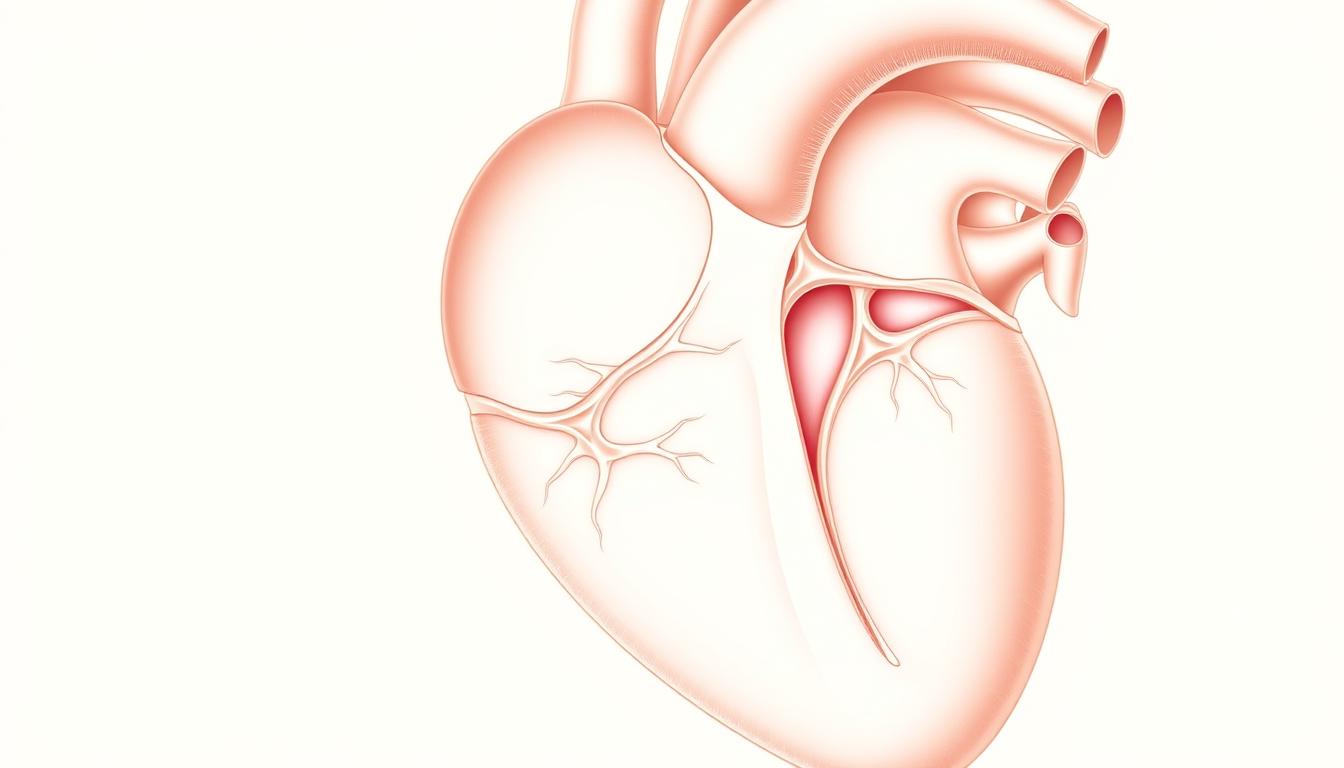
The moderator band, also known as septomarginal trabecula, is a band of cardiac muscle in the right ventricle. It is key to the heart’s function, mainly in the anatomical area of the right ventricle.
In the right ventricle, the moderator band is a muscular band. It runs from the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the ventricular septum. This is in a specific anatomical area. It’s important in some animals and humans, linked to the hypogastric region.
The moderator band’s function is critical for the heart’s performance. Knowing its role helps us understand cardiac anatomy and its functions.
Anatomical Overview of the Moderator Band
The moderator band has fascinated scientists for centuries. It was first described by Leonardo da Vinci. This band is a muscular structure in the right ventricle of the heart.
Definition and Location in the Right Ventricle
The moderator band connects the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the ventricular septum. It’s important for the heart’s electrical impulses.
Historical Discovery and Nomenclature
Leonardo da Vinci was one of the first to notice the moderator band. His work on the heart’s anatomy is significant.
Leonardo da Vinci’s Early Observations
Da Vinci’s detailed drawings showed the moderator band’s role in the heart. His work helped pave the way for further study.
Evolution of Terminology
The name for the moderator band has changed over time. Da Vinci first described it, and later it was called “trabecula septomarginalis.” This name reflects its connection to the septum and the right ventricle’s wall.
| Terminology | Description | Historical Context |
|---|---|---|
| Moderator Band | A muscular band in the right ventricle | Commonly used in clinical practice |
| Trabecula Septomarginalis | Anatomical term for the moderator band | Used in detailed anatomical descriptions |
Embryological Development of the Trabecula Septomarginalis
Learning about the trabecula septomarginalis’s growth helps us understand its role. It grows with the heart, which is key in cardiac development.
Formation During Cardiac Embryogenesis
The trabecula septomarginalis starts to form early in heart development. Cardiac embryogenesis is a complex process. It involves cell movement, change, and organization. These steps help create the heart’s parts, including the trabecula septomarginalis.
Developmental Timeline and Milestones
The growth of the trabecula septomarginalis happens in stages. Important milestones include its initial formation and growth.
First Trimester Development
In the first trimester, the heart changes a lot. This includes the start of the trabecula septomarginalis. It’s a key time for the heart’s structure to form.
Maturation Process
As the heart grows, the trabecula septomarginalis gets more important. It matures by changing myocardial cells and organizing conduction tissue.
| Developmental Stage | Key Features |
|---|---|
| First Trimester | Initial formation of trabecula septomarginalis |
| Maturation Phase | Differentiation and organization of myocardial and conduction tissue |
The growth of the trabecula septomarginalis is complex and well-controlled. Knowing about it helps us understand heart development and function. This is important, as heart issues can sometimes cause pain in the lower abdomen and pubic area.
Histological Composition and Structure
To understand the moderator band, we must look at its parts. The moderator band, or trabecula septomarginalis, is key in the heart’s electrical system. It helps the heart work right, just like the pelvis keeps the abdominal cavity stable.
Myocardial Components
The moderator band is made mainly of myocardial cells. These cells are vital for its ability to contract. They are similar to those in other heart parts, showing the band’s mechanical support role.
Purkinje Fibers and Conduction Tissue
The band also has Purkinje fibers for fast electrical signals. These fibers help the ventricles contract together efficiently. This is key for the heart to work well.
Connective Tissue Elements
The band also has connective tissue for support. This tissue keeps the band strong and working right in the heart. It’s like the tissues in the abdominal cavity that support it.
A famous cardiologist said, “The detailed makeup of the moderator band shows its big role in heart function.”
“The moderator band’s structure is a testament to the heart’s complex anatomy.”
Primary Physiological Functions
The moderator band is key in the heart, helping with electrical signals and support. It’s vital for the right ventricle to work right.
Electrical Conduction Role
The moderator band is important for the heart’s electrical system. It has parts of the right bundle branch. This is needed for the right ventricle to contract together.
Right Bundle Branch Transmission
The right bundle branch goes through the moderator band. It helps send electrical signals fast to the ventricles. This makes sure they contract together.
Ventricular Depolarization Patterns
The moderator band helps electrical signals spread evenly. This leads to better contraction and more efficient heart work.
Mechanical Support Functions
The moderator band also supports the right ventricle mechanically. It stops it from getting too big and keeps the papillary muscles steady.
Prevention of Ventricular Overdistension
The moderator band connects the septum to the right ventricle’s wall. It stops the ventricle from getting too big during relaxation.
Papillary Muscle Stabilization
The moderator band also helps keep the papillary muscles stable. These muscles are key for the tricuspid valve to close right during heart contraction.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical Conduction | Facilitates right bundle branch transmission and influences ventricular depolarization patterns. |
| Mechanical Support | Prevents ventricular overdistension and stabilizes papillary muscles. |
In conclusion, the moderator band is vital for the heart’s electrical and mechanical needs. It shows how important it is for heart health. The hypogastric region and pelvic area aren’t directly linked, but knowing about the moderator band helps us understand the heart better.
Secondary Physiological Functions
The moderator band has roles beyond its main functions. These secondary roles are key for the heart’s performance. They help the heart work more efficiently and effectively.
Contribution to Ventricular Contraction Efficiency
The moderator band helps improve how well the ventricle contracts. It makes sure blood moves well into the lungs. This is important for the heart to pump blood well.
Role in Maintaining Cardiac Output
The moderator band also helps keep the heart’s output steady. It makes sure electrical signals reach the heart muscle quickly. This helps the heart pump blood consistently.
Influence on Blood Circulation Dynamics
The moderator band affects how blood flows through the body. It helps the heart beat in sync with the body’s needs. This ensures blood flows as needed.
In summary, the moderator band’s secondary functions are vital for the heart. They impact how well the ventricle contracts, the heart’s output, and blood flow. Knowing these roles helps us understand the heart’s complex workings.
Clinical Significance in Cardiac Examination
The moderator band is important in heart exams. It can be seen through different imaging methods. This is key for a full heart check-up.
Echocardiographic Visualization
Echocardiography is a main tool for seeing the moderator band. It helps measure the band’s size, shape, and where it connects in the right ventricle.
Echocardiographic views like the parasternal short-axis and apical four-chamber views are best for seeing the moderator band.
MRI and CT Imaging Characteristics
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans give detailed pictures of the moderator band. They help spot heart problems.
These scans show clear images. They help find any unusual shapes or sizes of the moderator band.
Normal Variants and Measurements
Knowing what’s normal for the moderator band is key for correct diagnosis.
Research has set standards for the size and thickness of the moderator band in healthy people.
| Imaging Modality | Characteristics | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Assesses size, shape, and attachment | Primary diagnostic tool |
| MRI | High-resolution images of anatomy | Detailed anatomical assessment |
| CT | Detailed images of cardiac structures | Comprehensive cardiac evaluation |
Pathological Conditions Affecting the Moderator Band
The moderator band can face many health issues, both from birth and later on. These problems can change how the band works and might cause heart problems.
Congenital Abnormalities
Some heart defects are present at birth. These can affect the moderator band’s growth and function.
Hypoplasia and Hyperplasia
Hypoplasia means the band is not fully grown. This can lead to issues with electrical signals or support. On the other hand, hyperplasia means the band is too big. This can block the way or cause wrong electrical paths.
Association with Other Cardiac Defects
Often, the moderator band is not alone in its problems. It’s usually linked with other heart defects. For example, in Tetralogy of Fallot or other complex heart diseases, the band is often affected.
Acquired Conditions
Later in life, the moderator band can also face issues. These can change how it works.
Ischemic Changes
Coronary artery disease can harm the moderator band. Its blood supply, mainly from the right coronary artery, makes it vulnerable to damage.
Inflammatory Processes
Myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart, can also hit the moderator band. This inflammation can cause scarring and affect how the band conducts electrical signals.
| Condition | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Congenital Hypoplasia | Underdevelopment of the moderator band | Inadequate electrical conduction or mechanical support |
| Congenital Hyperplasia | Overdevelopment of the moderator band | Obstruction or abnormal conduction pathways |
| Ischemic Changes | Damage due to reduced blood flow | Dysfunction of the moderator band |
| Inflammatory Processes | Inflammation affecting the moderator band | Scarring and possible conduction issues |
It’s important to know about these health issues to diagnose and treat heart diseases related to the moderator band. The mix of birth defects and later problems shows why a full heart check is needed.
The Hypogastric Region: Anatomical Context
The hypogastric region, also known as the lower abdominal region, is full of important features. It’s key in both medical and scientific studies because of its complex structure and vital functions.
Definition and Boundaries
The hypogastric region is below the umbilical area and between the right and left iliac regions. Knowing its boundaries helps us understand the structures within it.
Major Structures and Organs
This area is home to vital structures and organs. These include parts of the urinary system, reproductive organs, and segments of the gastrointestinal tract. The specific contents can differ based on gender and individual.
| System | Structures/Organs |
|---|---|
| Urinary | Bladder, parts of the ureters |
| Reproductive | Uterus, ovaries, parts of the fallopian tubes in females; prostate gland, seminal vesicles in males |
| Gastrointestinal | Parts of the small intestine, sigmoid colon, rectum |
Vascular Supply Patterns
The blood supply to the hypogastric region is complex. It involves branches from the aorta and various iliac arteries. Knowing these patterns is vital for surgeries and diagnostic tests.
The blood supply includes branches from the common iliac arteries. These divide into internal and external iliac arteries. The internal iliac arteries supply the pelvic organs. The external iliac arteries mainly supply the lower limbs.
Cardiovascular Connections to the Hypogastric Region
It’s important to know how the heart and the hypogastric region are connected. This area in the pelvic area needs the heart’s help to stay healthy. The heart’s work is key for the hypogastric region’s health.
Cardiac Output Effects on Regional Perfusion
How well the heart pumps affects the hypogastric region’s blood flow. A strong heart means better blood flow to this anatomical area. This is vital for its functions.
“The balance between cardiac output and peripheral resistance determines the blood pressure and flow to various regions, including the hypogastric area.”
Hemodynamic Relationships
The heart and the hypogastric region have a complex relationship. Changes in heart function can change blood pressure and flow. This affects the whole body’s hemodynamic stability.
Clinical Implications of Altered Cardiac Function
When the heart doesn’t work right, it can harm the hypogastric region. Less blood flow can cause problems like ischemia. It’s important to understand these effects to treat related issues.
In summary, the heart’s connection to the hypogastric region is vital for health. More research can help us better treat related problems.
Diagnostic Approaches for Moderator Band Assessment
Figuring out problems with the moderator band needs a mix of methods. We use different ways to check its shape and how it works.
Physical Examination Limitations
Checking the moderator band with a physical exam is hard. It’s inside the right ventricle. So, we can’t use simple checks like feeling or listening with a stethoscope. We need more advanced tools.
Imaging Modalities and Protocols
Imaging techniques are key to seeing the moderator band. Echocardiography is great because it’s non-invasive and shows things in real-time. MRI and CT scans give detailed pictures and are good for tricky cases. We use special ways to make the moderator band show up better.
Electrophysiological Studies
Electrophysiological studies help us understand the moderator band’s electrical work. These studies show how the band affects the heart’s electrical signals. ECG and invasive tests give us important info about its function.
To sum up, using imaging and electrophysiological studies together is key. They help us get a full picture of the moderator band, making up for the limits of physical exams.
Surgical Considerations Involving the Moderator Band
In the world of congenital heart surgery, the moderator band is key. It plays a big role in how the heart works. Surgeons must pay close attention to it.
Relevance in Congenital Heart Surgery
The moderator band is important in heart defects. Surgeons need to know a lot about it. They must think about it when they plan and do surgeries.
Procedural Approaches and Techniques
There are many ways to handle the moderator band in surgery. Preserving it is often the goal. This helps the heart work better. Surgeons use special tools to see the band clearly during surgery.
Post-surgical Functional Outcomes
How well a surgery goes can affect the heart. Studies show that keeping the moderator band can make the heart work better. It can also lower the chance of problems.
| Surgical Approach | Outcome | Complication Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Preservation of Moderator Band | Improved Cardiac Function | Lower |
| Dissection without Preservation | Reduced Cardiac Efficiency | Higher |
It’s important to know how different surgeries affect the moderator band. This helps make sure patients do well. Even though we’re talking about heart surgery, it’s good to remember that the belly and heart can be connected. This shows why taking care of the whole body is important.
Research Developments in Moderator Band Understanding
Scientists are learning more about the moderator band, a part of the right ventricle. It’s important in how the heart sends electrical signals and supports its function. This area is getting a lot of attention in cardiology.
Recent Scientific Discoveries
Studies have found that the moderator band is made of special fibers. These fibers help the heart’s electrical system work well. This is a big discovery for heart health.
Emerging Functional Theories
New ideas suggest the moderator band might do more than we thought. It could help the heart contract more efficiently. Some research links its structure to better heart function, including the hypogastric region and its blood supply.
Technological Advances in Visualization
New imaging tools like MRI and echocardiography are helping us see the moderator band better. These tools let us study its shape and how it works. This knowledge is key to keeping the heart healthy, focusing on the pubic region and its related structures.
| Imaging Modality | Resolution | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| MRI | High | Detailed anatomical visualization |
| Echocardiography | Moderate | Non-invasive, real-time imaging |
| CT Scan | High | Rapid imaging, high resolution |
Comparative Anatomy Across Species
The moderator band is a key part of the heart that shows interesting changes in different animals. These changes help us understand how the heart has evolved and works. It shows how the heart’s structure can change and adapt.
Evolutionary Perspectives
The moderator band likely developed as hearts got more complex in higher animals. It appears in various ways in different species. This shows how different pressures have shaped the heart’s anatomy over time. Research suggests it’s more noticeable in active, fast animals that need a strong heart.
Functional Adaptations in Different Mammals
In different mammals, the moderator band changes to meet their needs. For example, big animals like cows and horses have a more visible moderator band. This might help their large hearts conduct electricity better. Smaller animals, like rodents, have a less visible moderator band. This could be because their hearts beat faster and work differently.
Comparative Physiological Significance
The moderator band’s role is to help hearts work well in all kinds of animals. By looking at how it changes, scientists learn about heart adaptations. This knowledge helps us understand human heart health and diseases, too.
Clinical Case Studies and Observations
Studies on the moderator band have greatly improved our understanding of its role in the heart. These studies give us important insights into diagnosing and treating heart problems. They also show how these issues affect the heart’s function.
Documented Anomalies and Their Presentations
Many studies have found unusual cases of the moderator band. These include it being missing, having a duplicate, or being connected in strange ways. Such issues can cause a range of symptoms, from none at all to serious heart problems. For example, a missing moderator band might lead to irregular heartbeats.
| Anomaly | Clinical Presentation | Management Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Absent Moderator Band | Ventricular Arrhythmias | Anti-arrhythmic Medication |
| Duplicated Moderator Band | Asymptomatic | Monitoring |
| Abnormal Connections | Conduction Disturbances | Pacemaker Implantation |
Treatment Approaches and Outcomes
How to treat the moderator band depends on the problem and its effects. Some cases need only watching, while others might need stronger treatments. This could be medicine or even surgery.
Learning Points for Clinical Practice
Studies on the moderator band teach us a lot for doctors. They show how important it is to think about these heart issues when diagnosing. They also remind us to tailor treatments to each patient’s unique situation.
Conclusion
The moderator band, or trabecula septomarginalis, is key in the heart’s structure and function. It affects how the heart beats and moves. Knowing about it helps us understand the heart’s complex workings and its role in health and disease.
The area around the moderator band is also important. It shows how the heart connects to the rest of the body, including the abdominal cavity. This cavity houses many vital organs and structures.
In summary, the moderator band is vital for the heart’s pumping efficiency. It ensures the heart works well, which is essential for our health. More research and awareness about it are needed.