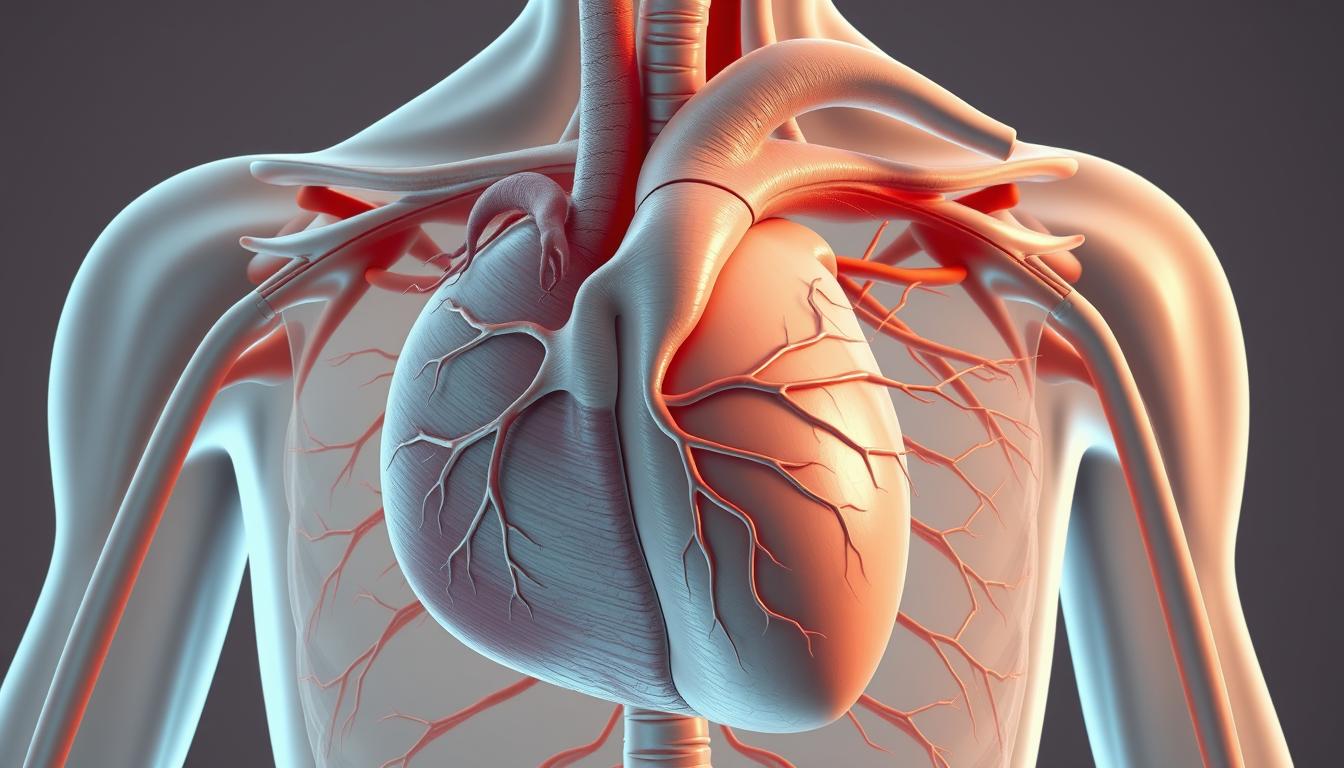
The Trabecula Septomarginalis, also known as the moderator band, is key in the heart’s ventricular septum. It’s a muscular band linking the interventricular septum to the right ventricle’s anterior wall.
This structure is vital in cardiac anatomy and ties closely to the heart’s electrical system. Knowing about the Trabecula Septomarginalis helps us understand heart development and how it works.
In this article, we’ll explore the anatomy, function, and clinical importance of the Trabecula Septomarginalis. We aim to give a detailed look at its role in heart development.
Anatomical Significance and Discovery
The Trabecula Septomarginalis, or moderator band, has been key in heart function. Its discovery helped us understand the heart’s complex anatomy, focusing on the ventricular septum.
Historical Context and First Descriptions
The Trabecula Septomarginalis was first noted for its role in the heart. Early scientists saw its importance in the ventricular septum and its effect on heart conduction.
Nomenclature Evolution
The names for the Trabecula Septomarginalis have changed over time. It was once known mainly for its moderating function. Different places have called it by various names.
Regional Terminology Differences
Different places use different names for it. Some call it the “moderator band,” while others use “Trabecula Septomarginalis.” This shows how complex heart anatomy terms can be.
Historical Name Changes
Over time, the name has changed several times. This reflects our growing understanding of its role in heart anatomy. Below is a table showing some of these names and what they mean.
| Historical Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Moderator Band | Named for its role in moderating electrical activity in the heart. |
| Trabecula Septomarginalis | Refers to its location and structure within the ventricular septum. |
Embryological Development of the Heart
Understanding how the heart develops is key to grasping its complex structure and function. The heart’s formation involves many steps, like cardiac looping and septation. These are vital for creating the ventricular septum.
Cardiac Looping and Septation
Cardiac looping is when the heart tube bends and folds. This sets the stage for the heart’s chamber development. Then, septation happens, where septa form to divide the heart into different chambers. Septation is a critical step for separating blood flow between chambers.
Formation of Ventricular Structures
The creation of ventricular structures is a complex process. It involves the growth and differentiation of cardiac cells. Molecular signals play a key role in guiding this process, ensuring the ventricular septum and other structures develop right.
Timeline of Development
The heart’s development is a well-coordinated process that takes several weeks. Important milestones include the heart tube’s formation, cardiac looping, and septation.
Molecular Signals Guiding Formation
Molecular signals, like growth factors and transcription factors, direct the heart’s structure formation.
“The precise regulation of these signals is essential for normal heart development.”
Any problem with these signals can cause congenital heart defects.
Trabecula Septomarginalis
The Trabecula Septomarginalis, or moderator band, is a muscle in the right ventricle. It’s key for the heart’s electrical system and how it works.
Detailed Structural Anatomy
This structure is made of muscle. It runs from the septum to the right ventricle’s front wall. It also has part of the bundle of His, which is important for electrical signals.
Key Components:
- Muscular structure
- Connection between the interventricular septum and the right ventricular wall
- Contains part of the bundle of His
Dimensional Characteristics
The size and shape of the Trabecula Septomarginalis differ from person to person. Knowing these differences is important for studying anatomy and for medical use.
Average Measurements in Adults
Research shows it’s usually 1.5 to 2.5 cm long in adults. But, size can change with age, sex, and heart size.
Variations in Size and Shape
How big or small the Trabecula Septomarginalis is can affect the heart’s performance. Some people have a more noticeable moderator band, while others don’t.
The Trabecula Septomarginalis is a vital part of the heart’s function. Its differences among people show how complex the heart’s anatomy is.
Relationship to Cardiac Conduction System
The Trabecula Septomarginalis is key in the cardiac conduction system. It helps electrical impulses move quickly, keeping the heart rhythm steady.
This part of the heart is special because of its structure and where it is. It has Purkinje fibers, which are important for fast electrical signal travel.
Purkinje Fiber Distribution
The Purkinje fibers in the Trabecula Septomarginalis are vital. They help the heart beat in sync.
- Purkinje fibers spread out in the ventricular walls.
- The Trabecula Septomarginalis helps these fibers move electrical signals well.
Electrical Propagation Patterns
The Trabecula Septomarginalis shapes how electrical signals move through the heart. It helps signals go fast from the atrioventricular node to the ventricles.
Conduction Velocities
The conduction velocities in the Trabecula Septomarginalis are very fast. This allows the ventricles to contract together.
Electrophysiological Properties
The electrophysiological properties of the Trabecula Septomarginalis are important. They help keep the heart rhythm normal by efficiently sending electrical signals.
The Moderator Band: Functional Equivalent
The moderator band is a key part of the right ventricle, affecting how well the heart works. It’s a muscular band that links the interventricular septum to the right ventricle’s anterior wall.
Studies in comparative anatomy show the moderator band is more noticeable in some species. This highlights its importance in evolution.
Comparative Anatomy
The moderator band is not just for humans; it’s found in many other animals too. Comparative anatomy shows its size and presence vary. This often matches the animal’s activity level and heart needs.
In some animals, the moderator band is more developed. This suggests it has a special role in heart function.
Functional Similarities and Differences
The moderator band is vital for the cardiac function of the right ventricle. It helps the ventricle contract and prevents it from getting too big during contraction.
Right Ventricular Moderator Band
In the right ventricle, the moderator band is well-developed. It contains Purkinje fibers, which are key for fast electrical signal transmission.
Left Ventricular Structures
The left ventricle doesn’t have a distinct moderator band. Instead, it has a complex muscle arrangement. This makes its walls thicker and its contraction stronger.
| Characteristics | Right Ventricle | Left Ventricle |
|---|---|---|
| Moderator Band Presence | Present | Absent |
| Function | Aids in contraction and prevents dilation | Thicker walls for greater contractile force |
The left ventricle’s equivalent to the moderator band is its complex muscle setup. This setup ensures the heart works efficiently.
Histological Composition of Heart Ventricles
Heart ventricles are made up of complex layers. These layers are supported by a framework of connective tissue. This structure is key for the heart to work well.
Myocardial Arrangement
The heart’s ventricles have a special way of arranging their muscle. This setup helps the heart pump blood well across the body.
The muscle fibers are arranged to make the heart strong. This ensures the heart can handle different situations.
Connective Tissue Framework
The connective tissue framework supports the heart’s muscle. It helps the muscle keep its shape and work well under stress.
Collagen Distribution
Collagen is a big part of this framework. It’s spread out in the muscle to add strength and flexibility.
The way collagen is placed is very important. It helps the heart work right without getting in the way of its muscle movements.
Cellular Organization
The heart’s muscle cells are very organized. They are set up to help the heart beat in sync and pump blood well.
This organization is vital. It makes sure the heart’s ventricles work together to pump blood efficiently.
| Component | Function | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Myocardium | Contractile element | Highly organized, contractile fibers |
| Connective Tissue | Structural support | Collagen-rich, provides strength and elasticity |
| Collagen | Strength and elasticity | Carefully distributed throughout myocardium |
Physiological Role in Cardiac Function
The Trabecula Septomarginalis is key to the heart’s function. It helps the ventricles contract and pump blood. This is essential for the heart’s efficiency.
Mechanical Support During Contraction
The Trabecula Septomarginalis gives mechanical support to the ventricles. This support is vital for pumping blood well. It helps the heart work at its best.
Contribution to Ventricular Dynamics
This structure greatly affects ventricular dynamics. It changes how pressure and volume work in the ventricles. This impacts the heart’s pumping ability.
Pressure-Volume Relationships
Its role in pressure-volume relationships is critical. It helps control how much blood is pumped during contraction. This is key for the heart’s function.
Impact on Ejection Fraction
The Trabecula Septomarginalis also affects the ejection fraction. This is a measure of heart health. It ensures the heart pumps blood well, supporting its function.
In summary, the Trabecula Septomarginalis is essential for the heart. It provides mechanical support and affects ventricular dynamics. Its role in pressure-volume relationships and ejection fraction highlights its importance for efficient heart function.
Imaging Techniques for Ventricular Septum
Imaging techniques have changed how we look at the ventricular septum. This part of the heart is key to its function. Seeing it clearly is vital for diagnosing and treating heart issues.
Echocardiographic Assessment
Echocardiography is a non-invasive way to check the ventricular septum. It shows the septum’s thickness, movement, and any defects. Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) is often used first. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) gives more detailed views, mainly during surgeries.
Advanced Cardiac Imaging
There are more advanced imaging methods for the ventricular septum. These include:
MRI Visualization Protocols
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) gives clear pictures of the heart. It lets us see the septum in detail. Cine MRI and late gadolinium enhancement help check the septum’s movement and find scars.
CT Angiography Applications
Computed Tomography (CT) angiography is also useful for the ventricular septum. It’s great for looking at congenital heart defects or planning treatments. It shows detailed anatomy and helps spot septal defects and other issues.
The table below shows the main points of the imaging methods we talked about:
| Imaging Modality | Key Features | Clinical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Echocardiography | Non-invasive, real-time imaging | Initial assessment, septal defect detection |
| MRI | High-resolution, tissue characterization | Detailed septal evaluation, fibrosis detection |
| CT Angiography | Rapid, detailed anatomical imaging | Congenital heart defect assessment, pre-procedural planning |
Congenital Heart Defects Involving Septal Structures
It’s key to know about congenital heart defects that affect septal structures. These issues can really mess with the heart’s function and health.
Ventricular Septal Defects Classification
Ventricular septal defects (VSDs) have an opening in the ventricular septum. This lets blood move between the ventricles. VSDs are sorted by where and how big they are.
- Perimembranous VSDs: Near the aortic, mitral, and tricuspid valves.
- Muscular VSDs: In the muscular part of the septum.
- Subarterial VSDs: Under the arterial valves.
Tetralogy of Fallot Pathophysiology
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a complex heart defect. It has four main parts: VSD, pulmonary stenosis, right ventricular hypertrophy, and an overriding aorta. It changes how blood flows and gets oxygen.
Anatomical Variations
TOF can vary in how severe the pulmonary stenosis is and if there are more VSDs.
Hemodynamic Consequences
TOF’s effects include less blood to the lungs and more work for the right ventricle. This leads to hypertrophy.
| Defect | Characteristics | Hemodynamic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Ventricular Septal Defect | Opening in ventricular septum | Left-to-right shunt |
| Tetralogy of Fallot | VSD, pulmonary stenosis, RVH, overriding aorta | Reduced pulmonary blood flow, RV hypertrophy |
Congenital heart defects involving septal structures need careful diagnosis and treatment. Knowing about these defects is key to managing them well.
Clinical Significance in Cardiac Arrhythmias
Understanding the Trabecula Septomarginalis is key to diagnosing and treating cardiac arrhythmias. This part of the heart, also known as the moderator band, is vital for the heart’s electrical system.
Ventricular Tachycardia Origins
Ventricular tachycardia can start in different parts of the heart, including the Trabecula Septomarginalis. The structure’s role in the heart’s electrical pathways is why it’s linked to ventricular tachycardia. Research shows it can cause abnormal electrical activity.
Bundle Branch Blocks
The Trabecula Septomarginalis is also important in bundle branch blocks. It’s connected to the bundle branches, which are key for the heart’s electrical system. Damage here can lead to bundle branch blocks and various heart problems.
Electrocardiographic Findings
ECG findings are vital for diagnosing Trabecula Septomarginalis and bundle branch block issues. An ECG can show signs of ventricular tachycardia or bundle branch blocks.
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for Trabecula Septomarginalis issues depends on the diagnosis. Catheter ablation is often used for ventricular tachycardia from this area. For bundle branch blocks, treatment aims to fix the cause or manage symptoms.
| Condition | ECG Findings | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Ventricular Tachycardia | Wide QRS complex, AV dissociation | Catheter ablation, anti-arrhythmic drugs |
| Bundle Branch Blocks | Wide QRS complex, specific patterns for left or right bundle branch block | Pacemaker implantation, cardiac resynchronization therapy |
Surgical Considerations in Cardiac Procedures
Cardiac procedures are complex and need careful planning before and during surgery. Modern cardiac surgery focuses on keeping important parts of the heart safe, like the Trabecula Septomarginalis.
Preoperative Anatomical Assessment
Understanding the heart’s layout is key before surgery. Advanced imaging helps see the heart’s details and spot any issues that might affect the surgery.
Imaging modalities like MRI and CT scans give surgeons a clear picture of the heart. They help plan the surgery. The Trabecula Septomarginalis is a key structure that surgeons must think about before starting.
Intraoperative Navigation
Navigation during surgery is also vital. It helps surgeons find and protect important parts of the heart. New navigation tools and live images guide the team.
Surgical Approaches
The surgical method chosen can greatly affect the outcome. Surgeons pick the best approach based on the patient’s heart and the surgery’s needs.
Preservation Techniques
Keeping the heart’s structures intact is essential for good heart function after surgery. Methods that reduce damage to the heart and other key areas are vital.
| Surgical Consideration | Importance | Techniques |
|---|---|---|
| Preoperative Assessment | High | Advanced Imaging |
| Intraoperative Navigation | High | Real-time Imaging, Navigation Systems |
| Preservation of Trabecula Septomarginalis | Critical | Careful Dissection, Minimally Invasive Techniques |
By planning carefully before surgery and using precise navigation during it, surgeons can greatly improve results. Keeping structures like the Trabecula Septomarginalis safe is key for the heart’s function and the surgery’s success.
Interventional Cardiology Perspectives
Catheter-based procedures and device implantation are key in interventional cardiology. They need exact knowledge of the heart’s anatomy. The Trabecula Septomarginalis is very important in these procedures. It helps us understand the heart’s septum.
Catheter-Based Procedures
Catheter-based procedures have gotten much better. They can now treat complex heart problems. These procedures go through the heart’s chambers. Knowing the Trabecula Septomarginalis’s anatomy is very important.
Device Implantation Considerations
When putting in devices like pacemakers, careful planning is needed. The device’s placement must consider the heart’s anatomy. This ensures it works well and avoids problems.
Lead Placement Strategies
Placing leads is a big part of device implantation. The plan for lead placement must consider the patient’s anatomy. This includes the Trabecula Septomarginalis’s location. It helps get the best pacing and sensing.
Complication Avoidance
To avoid problems during device implantation, knowing the risks is key. Careful planning before and monitoring during the procedure helps. This way, complications can be kept to a minimum.
In summary, understanding the heart’s anatomy is vital in interventional cardiology. Knowing about the Trabecula Septomarginalis is essential for success in these procedures.
Comparative Anatomy Across Species
Studying the Trabecula Septomarginalis across different species helps us understand its evolution. This muscular part in the right ventricle shows big differences among mammals.
Evolutionary Development
The Trabecula Septomarginalis’s evolution is tied to how mammals adapt to their environments. In active animals, this structure is more developed. It helps the heart work better.
Mammalian Variations
Different mammals have unique Trabecula Septomarginalis features. For example, primates have a similar structure to humans. This shows their close evolutionary ties.
Primate Cardiac Structures
Research shows that primates have a Trabecula Septomarginalis like humans. This similarity is key for understanding human heart anatomy and its history.
Veterinary Significance
Studying the Trabecula Septomarginalis in various mammals is vital for animal health. It helps vets diagnose and treat heart problems in animals.
| Species | Trabecula Septomarginalis Characteristics | Veterinary Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Human | Prominent structure | Important for cardiac function |
| Primate | Similar to human | Relevant for human cardiac studies |
| Canine | Variable prominence | Important for diagnosing cardiac issues |
As a leading cardiac anatomist noted,
“The study of heart structures across species deepens our knowledge of human anatomy. It also reveals the evolutionary forces that have shaped the human heart.”
Recent Research Advances
Recent studies have made big strides in understanding the Trabecula Septomarginalis. They used computational modeling techniques. These advances help us better understand the heart’s anatomy and function.
Computational Modeling Studies
Computational modeling is a key tool in cardiac research. It lets us simulate how the heart works and the role of the Trabecula Septomarginalis. These models help us see how the Trabecula Septomarginalis affects the heart’s movement.
- Simulation of cardiac cycles to understand the mechanical support provided by the Trabecula Septomarginalis
- Analysis of electrical propagation patterns through the ventricular septum
Tissue Engineering Applications
Tissue engineering has seen big progress, mainly in fixing or replacing damaged heart tissues. The Trabecula Septomarginalis is a special case for tissue engineers because of its complex structure.
3D Bioprinting Developments
3D bioprinting is a major breakthrough in tissue engineering. It lets us make detailed tissue structures that look like real heart tissue. Scientists are using 3D bioprinting to make the Trabecula Septomarginalis and study it in a lab.
Regenerative Medicine Approaches
Regenerative medicine is exploring new ways to fix or grow damaged heart tissue, like the Trabecula Septomarginalis. It uses stem cells and biomaterials. These methods could help treat heart problems caused by structural issues.
Conclusion
The Trabecula Septomarginalis is key to the heart’s working. Its special shape and spot in the heart are vital. They help control the heart’s electrical signals and how it beats.
Knowing about the Trabecula Septomarginalis is important for doctors and scientists. It helps them spot and treat heart problems. This structure is linked to heart rhythm issues and defects.
More studies on the Trabecula Septomarginalis will help us understand heart health better. This knowledge will lead to better heart care and treatments. By studying the heart’s anatomy, we can improve how we treat patients.