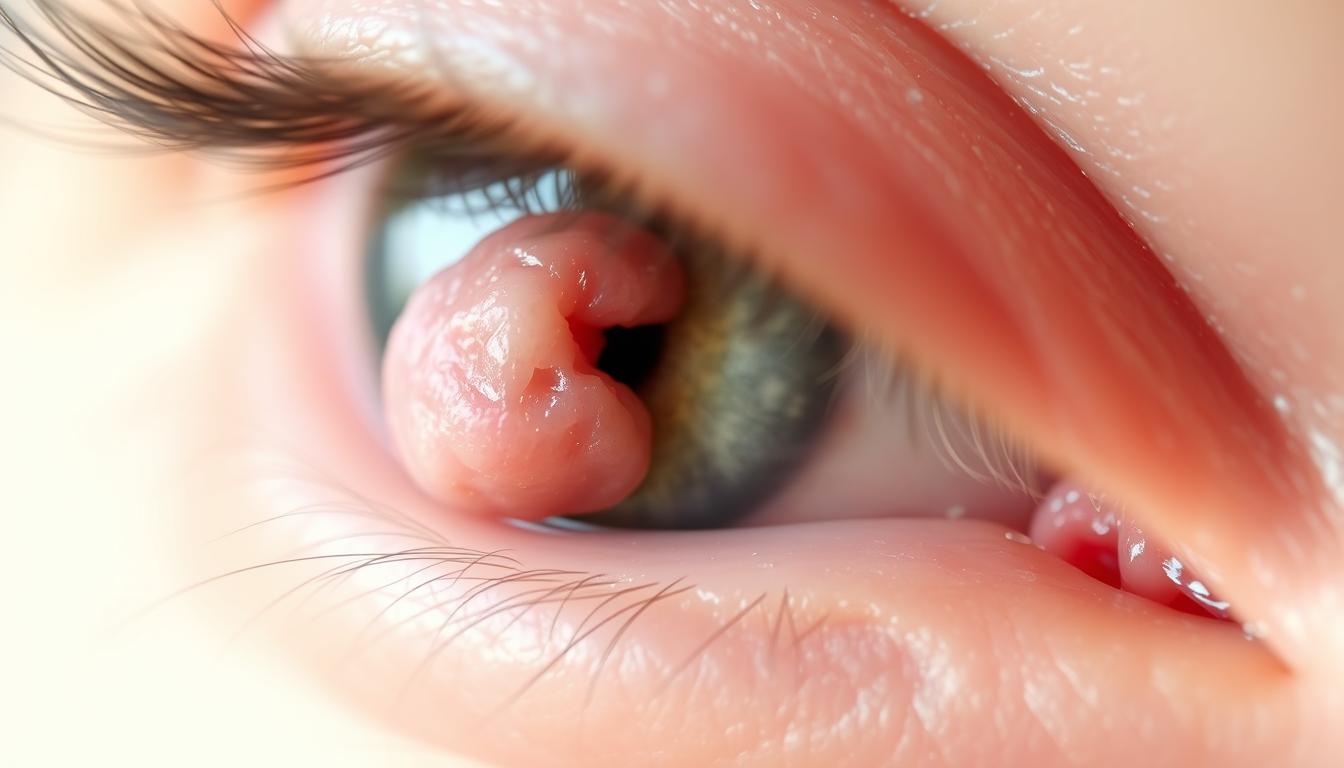
Eyelid papillomas are common benign eyelid tumors. They look like flesh-colored, pink, or dark brown spots on the eyelid.
These spots are usually harmless but can worry people. They might look bad or feel uncomfortable. An eyelid papilloma often shows up near the lateral horn of the eyelid. This area is important in the eyelid’s anatomy.
If you see unusual growths on your eyelids, it’s key to know about eyelid papilloma. Even though they’re not harmful, seeing a doctor is a good idea. They can help figure out what it is and what to do next.
The Lateral Horn Defined
The lateral horn is very important in the autonomic nervous system. It’s a key part of the spinal cord, playing a big role in many autonomic functions.
Anatomical Location and Structure
The lateral horn is found in the spinal cord, mainly in the thoracic and upper lumbar areas. It’s a gray matter part of the autonomic nervous system. This system controls the body’s involuntary actions.
This area has a special group of neurons. These neurons send signals that help control things like heart rate and blood pressure.
Functional Overview
The lateral horn mainly works with the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. It helps control the body’s ‘fight or flight’ response and other autonomic functions.
- Regulation of heart rate and blood pressure
- Control of sweat glands and body temperature
- Influence on the dilation and constriction of blood vessels
The lateral horn’s neurons are key in these processes. They work together in a complex network within the nervous system.
Anatomical Position of the Lateral Horn in the Spinal Cord
The location of the lateral horn in the spinal cord is key to understanding its role. It is found in the gray matter of the spinal cord.
Gray Matter Organization
The gray matter in the spinal cord has different areas. The lateral horn is one of them. It mainly deals with the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system.
Segmental Distribution
The lateral horn is not spread out evenly in the spinal cord. It is mainly found in the thoracic and upper lumbar areas.
Relationship to Other Spinal Structures
The lateral horn is close to other parts of the spinal cord. These include the dorsal and ventral horns. Knowing these connections helps us understand the spinal cord’s function better.
| Region | Presence of Lateral Horn | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracic | Present | Sympathetic outflow |
| Upper Lumbar | Present | Sympathetic outflow |
| Cervical and Lower Lumbar | Absent | N/A |
The way the lateral horn is organized and distributed in the spinal cord shows its unique role. Its connection with other spinal structures also highlights its importance in neural function.
Cellular Composition of the Lateral Horn
The lateral horn is made up of different neurons and glial cells. These cells work together to help the lateral horn do its job. It’s a key part of the autonomic nervous system.
Neuron Types and Characteristics
The lateral horn has many types of interneurons. These neurons are special because of their unique shapes and jobs. They help move information around.
- Interneurons help connect different groups of neurons.
- They can take in and process lots of information.
Glial Cell Support
Glial cells in the lateral horn support the neurons. They keep the environment right for the neurons to work well. These cells are key for the health of the neurons.
Synaptic Organization
The way neurons connect in the lateral horn is complex. These connections are important for sending signals well. This helps the lateral horn work right.
The connections between neurons are tightly controlled. This control is vital for the lateral horn’s role in controlling the body.
The Lateral Horn’s Integration with the Nervous System
The lateral horn is key in linking the autonomic nervous system with the central and peripheral nervous systems. It’s vital for controlling functions like heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
Connections to the Central Nervous System
The lateral horn connects to the central nervous system through neural pathways. These paths let it get and process info from the brain, leading to coordinated responses. The central nervous system gives the lateral horn the inputs it needs to work well.
Research shows the lateral horn gets signals from the hypothalamus and brainstem. These signals are important for controlling autonomic functions based on the body’s state and surroundings.
“The lateral horn’s connection to the central nervous system is vital for maintaining homeostasis and enabling the body to respond to stress and other challenges.”
Interface with the Peripheral Nervous System
The lateral horn connects with the peripheral nervous system through preganglionic neurons. These neurons send signals to organs and tissues, controlling functions like heart rate and blood pressure.
| Function | Description | Neural Pathway |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rate Regulation | Modulation of heart rate in response to stress or physical activity | Lateral horn to sympathetic ganglia |
| Blood Pressure Control | Adjustment of blood vessel diameter to maintain blood pressure | Lateral horn to sympathetic ganglia |
Neural Pathway Mapping
Mapping neural pathways is key to understanding how the lateral horn works with the nervous system. By tracing connections, researchers learn about the complex interactions in autonomic regulation.
Advanced imaging has helped researchers map autonomic control pathways. These studies have given us insights into how the lateral horn interacts with other nervous system parts.
Role in the Autonomic Nervous System
The lateral horn is key in the autonomic nervous system. It controls the sympathetic division. This is vital for actions like heart rate, digestion, and breathing.
Sympathetic Division Control
The lateral horn is vital for the sympathetic division. It has neurons that send signals to sympathetic ganglia. This affects many body responses, like the ‘fight or flight’ response.
Parasympathetic Interactions
The lateral horn works with the parasympathetic division too. This balance is important for the body’s functions. For example, the parasympathetic division helps during rest, supporting recovery.
Autonomic Regulation Mechanisms
The lateral horn uses complex neural circuits to control the body. These circuits take in information from the brain and senses. This helps manage sympathetic and parasympathetic outputs.
| Division | Primary Functions | Key Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Sympathetic | Prepares body for ‘fight or flight’ | Increased heart rate, blood pressure |
| Parasympathetic | Promotes rest and digestion | Decreased heart rate, enhanced digestion |
Keeping the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions is essential. Problems with this balance can cause health issues. This shows how important the lateral horn is for our well-being.
Sensory Information Processing in the Lateral Horn
The lateral horn is key in handling sensory inputs that control the autonomic nervous system. It plays a big role in getting, mixing, and adjusting sensory info. This helps keep the body stable and reacts to outside changes.
Afferent Signal Reception
The lateral horn gets signals from all over the body. These signals tell it about the body’s state and what’s happening outside. Getting these signals is the first step in handling sensory info. It lets the lateral horn know what the body needs and how to react.
Sensory Integration Functions
The lateral horn mixes the sensory info with other neural signals to create the right autonomic responses. This mixing is done through complex neural paths and talks with other parts of the nervous system. It leads to a balanced response that keeps the body working well.
Modulation of Sensory Inputs
The lateral horn also changes how it gets sensory signals based on the body’s current state. It can make the signals stronger or weaker, affecting how the autonomic system responds. This adjusting is key for adapting to new situations, both inside and outside the body.
In short, the lateral horn’s job in handling sensory information is complex. It involves getting, mixing, and adjusting sensory inputs. This detailed work is vital for controlling the autonomic system and keeping the body in balance.
The Lateral Horn’s Contribution to Motor Functions
The lateral horn plays a key role in motor functions. It helps in sending signals to muscles and glands. This is vital for controlling different motor activities.
Efferent Signal Generation
Efferent signals are important for sending information from the brain to muscles and glands. The lateral horn is key in creating these signals. It focuses on the sympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system.
Key aspects of efferent signal generation include:
- Integration of inputs from various neural sources
- Processing and modulation of signals
- Transmission to motor neurons or other effectors
Coordination with Motor Neurons
The lateral horn works with motor neurons for precise control. It uses complex neural circuits. These circuits combine information from sensory inputs, the brain, and local networks.
Effective coordination is achieved through:
- Synaptic plasticity and adaptation
- Regulation of neurotransmitter release
- Modulation of neural excitability
Movement Regulation Mechanisms
The lateral horn helps regulate movement through the autonomic nervous system and motor neurons. It adjusts motor output based on sensory feedback and motor planning.
The regulation mechanisms include:
- Modulation of sympathetic and parasympathetic outputs
- Adjustment of motor neuron excitability
- Integration with other motor control systems
Interneurons of the Lateral Horn
Interneurons in the lateral horn play a key role in controlling neural pathways. They help integrate and process signals. This is important for the autonomic nervous system’s function.
Classification and Types
Interneurons in the lateral horn are divided based on their shape and function. Different types of interneurons have unique roles in processing neural signals. Knowing these types helps us understand the lateral horn’s complex interactions.
Functional Roles
Interneurons in the lateral horn regulate autonomic functions and control sensory inputs. They act as intermediaries between neural pathways. This helps in complex interactions within the nervous system.
Connectivity Patterns
The connections of interneurons in the lateral horn are complex and well-organized. These connections allow them to coordinate with other neurons. This affects both sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Understanding these connections is key to understanding the lateral horn’s role in neural function.
In conclusion, interneurons in the lateral horn are essential for its function. They add complexity and nuance to the autonomic nervous system. Further research will continue to highlight their importance.
Clinical Significance and Pathologies
The lateral horn is key in the autonomic nervous system. Its problems can cause many health issues. This is because the autonomic nervous system depends on the lateral horn for control.
Disorders Affecting the Lateral Horn
Many disorders can harm the lateral horn. These include:
- Multiple system atrophy
- Pure autonomic failure
- Autonomic dysreflexia
- Spinal cord injuries
These issues can mess up how the lateral horn works. This leads to problems with the autonomic nervous system.
Diagnostic Approaches
Doctors use different ways to find out if the lateral horn is affected. They look at:
- Autonomic function tests
- Imaging studies (MRI, CT scans)
- Electrophysiological assessments
These tools help doctors find the cause of the problem. Then, they can plan the right treatment.
Treatment Strategies
Doctors aim to manage symptoms and fix the root cause of problems with the lateral horn. They might use:
- Pharmacological interventions
- Lifestyle modifications
- Rehabilitation therapies
Knowing how the lateral horn works helps doctors treat patients better. This leads to better health outcomes.
Research Methodologies in Lateral Horn Studies
The lateral horn’s complex role in the nervous system is explored through advanced research methods. These methods help us understand its structure, function, and how it works with other parts of the nervous system.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques are key in studying the lateral horn. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) help us see the spinal cord’s anatomy. They show where the lateral horn is and how it connects with other spinal structures.
Electrophysiological Approaches
Electrophysiological methods are vital for understanding the lateral horn’s function. Electromyography (EMG) and local field potentials (LFP) recordings let researchers study neural activity. They help us see how the lateral horn handles sensory information and controls motor responses.
Molecular and Genetic Studies
Molecular and genetic studies give us a closer look at the lateral horn’s cells and how they connect. By studying the genes that control neuron development, researchers can uncover how different cells work together. Single-cell RNA sequencing helps identify specific neurons and their roles in controlling the body.
Using these research methods together has greatly improved our understanding of the lateral horn. It shows how it plays a part in the spinal cord and the autonomic nervous system. As research continues, we can learn even more about the lateral horn and its importance for our health.
Evolutionary Perspectives on the Lateral Horn
Comparative anatomy and developmental biology give us key insights into the lateral horn’s evolution. This part of the brain has evolved to be vital for sensory information and motor functions in many species.
Comparative Anatomy Across Species
Research in comparative anatomy reveals the lateral horn’s presence in various forms across species. This shows its essential role in the nervous system. For example, studies in rodents and primates have found both similarities and differences in the lateral horn’s structure. These differences suggest adaptations to different environments and needs.
Developmental Biology Insights
Developmental biology sheds light on the lateral horn’s evolutionary history. It shows that the lateral horn’s development is controlled by genetics and environment. A leading neuroscientist notes, “The developmental pathway of the lateral horn is a testament to the complex processes that shape the nervous system” (
A Developmental Perspective on the Nervous System
).
Evolutionary Adaptations
The lateral horn has evolved to improve its role in sensory processing and motor control. These changes are seen in the different forms of the lateral horn across species. Each variation has been shaped to meet specific needs.
In conclusion, studying the lateral horn’s evolution highlights its critical role in the nervous system. By exploring its history and adaptations, we can better understand its function and importance.
Future Directions in Lateral Horn Research
New technologies are changing how we study the lateral horn in the autonomic nervous system. Improvements in imaging, electrophysiology, and molecular biology will give us fresh insights. We’ll learn more about its structure and how it works.
Emerging Technologies
New tools are making lateral horn research more advanced. Single-cell RNA sequencing and optogenetics let researchers dive deep into its details.
Functional MRI is also helping us see how the lateral horn works in real life.
Potential Clinical Applications
Studying the lateral horn could lead to new treatments for neurological disorders. This includes:
- Creating new treatments for autonomic dysfunction
- Understanding pain better
- Improving care for spinal cord injuries
Unanswered Questions in the Field
Even with progress, many questions about the lateral horn remain. These include:
| Question | Potential Research Direction |
|---|---|
| What are the specific roles of different neuron types in the lateral horn? | Single-cell analysis and functional studies |
| How does the lateral horn integrate information from different sensory inputs? | Electrophysiological studies and neural circuit mapping |
| Can modulation of the lateral horn be used to treat autonomic dysfunction? | Clinical trials and translational research |
Answering these questions is key to understanding the lateral horn better. It will help us grasp its role in the nervous system.
Conclusion
The Lateral Horn is key to the spinal cord, playing a big role in how our body works. It helps control our autonomic nervous system. This is important for keeping our body balanced and reacting to the world around us.
This area of the spinal cord handles sensory info and sends out signals for movement. It works closely with other parts of the nervous system. This teamwork helps us move and respond to our environment.
Learning about the Lateral Horn is important for science and helping people with nerve problems. More research will show us how it works and how we can use it to help others.